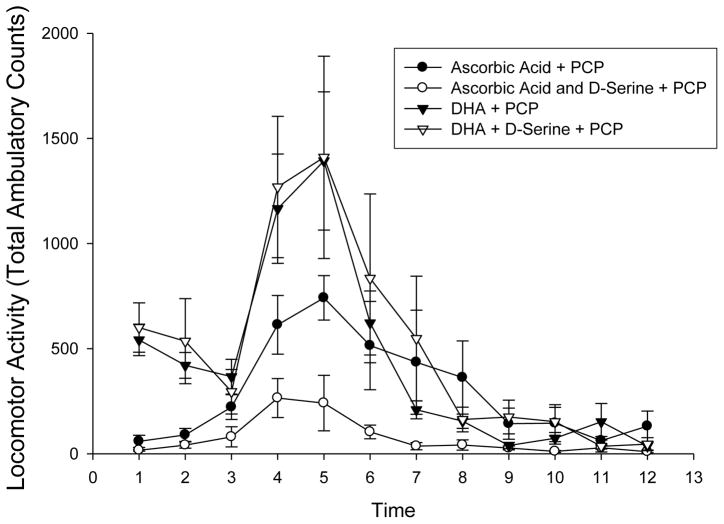
Fig 5.
Effect of ascorbic acid (300 mg/kg, i.p.) and docosahexanoic acid (DHA 50 mg/kg in 25% DMSO, i.p.) on PCP (5 mg/kg) induced locomotor activity. DHA + D-serine (▲) was not different than DHA alone (△), nor did DHA have an effect on locomotor activity (versus sal-sal +PCP (■) in figure 5). Ascorbic acid (●) and ascorbic acid + D-serine (○) further reduced the PCP-induced locomotor activity. Values are mean Total Ambulatory Counts taken in 10 minute segments (n =8) (p values for time segment 4–6, < 0.001 ascorbic acid vs saline (□ from Fig. 2); <0.01 ascorbic acid ● vs ascorbic acid + D-serine ○).