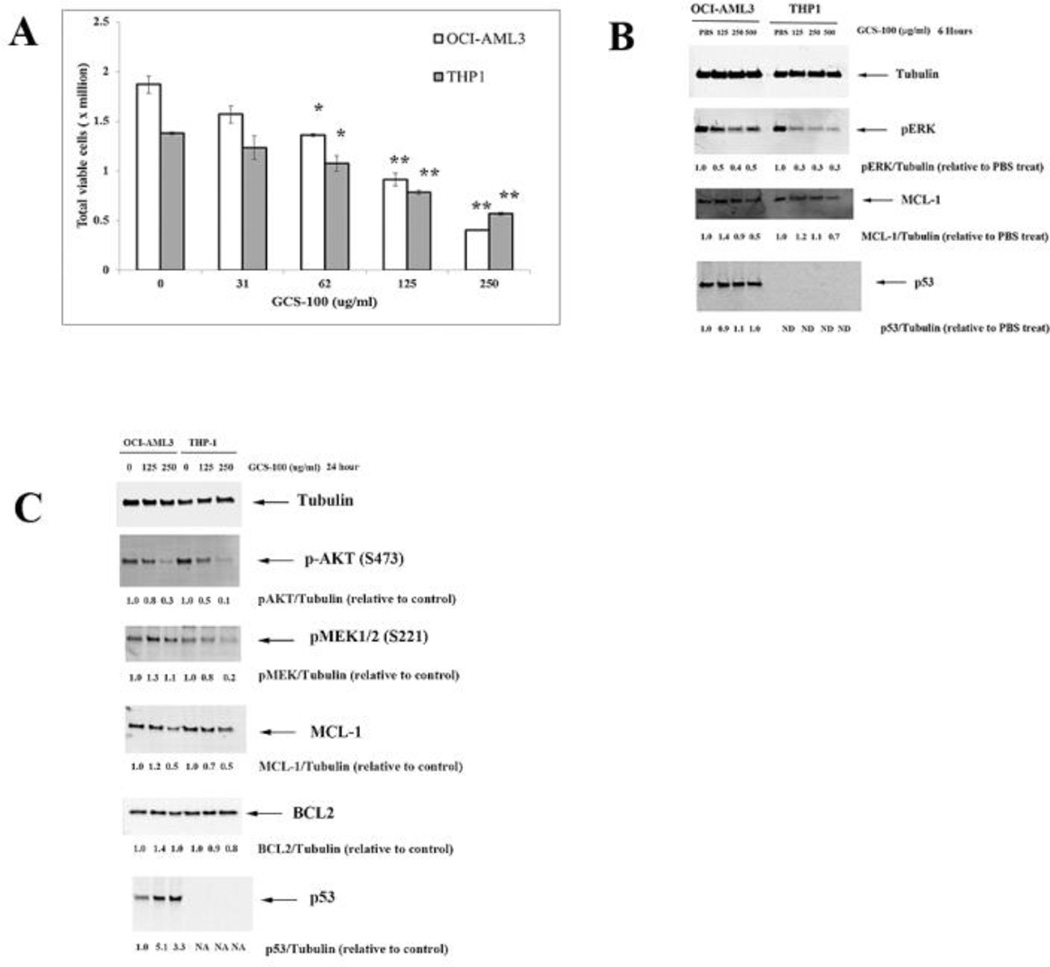
Fig. 1.
GCS-100 kills AML cells and inhibits ERK and AKT activation and MCL-1 expression. A. OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cells were treated with vehicle (10% PBS) or varying doses of GCS-100 for 72 h and cell viability assessed by trypan blue staining. * represents p < 0.05; ** represents p < 0.01 as determined by Student t test. B. OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cells were treated with vehicle (10% PBS) or varying doses of GCS-100 for 6 h, protein lysate isolated, and immunoblot analysis performed with antibodies against phosphorylated ERK, MCL-1, p53, and Tubulin. Ratio of protein expression to Tubulin loading control was determined by densitometry using LiCor imager. C. OCI-AML3 and THP-1 cells were treated with vehicle (10% PBS) or varying doses of GCS-100 for 24 h, protein lysate isolated, and immunoblot analysis performed with antibodies against phosphorylated AKT, phosphorylated MEK1, MCL-1, BCL2, p53, and Tubulin. Ratio of protein expression to Tubulin loading control was determined by densitometry using LiCor imager.