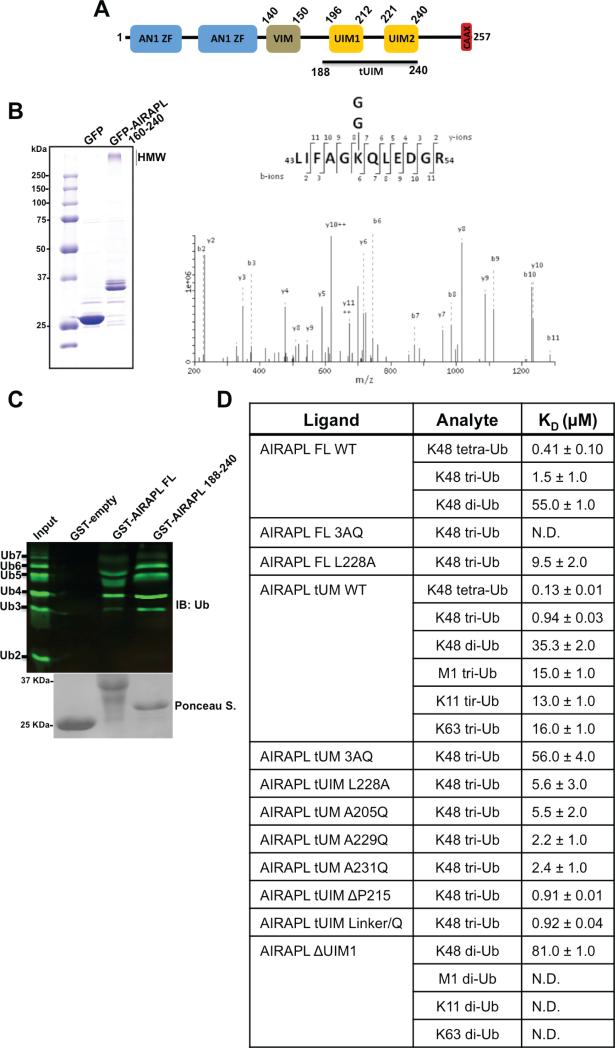
Figure 1. AIRAPL is an ubiquitin-binding protein and is selective for Lys48-linked ubiquitin chains.
(A) Schematic domain organization of mouse AIRAPL protein. AN1 ZF, AN1-type zinc finger; VIM, valosin-containing protein (VCP)-interacting motif; UIM, ubiquitin-interacting motif; CAAX box, a sequence of cysaliphatic-aliphatic-undefined amino acids. (B) Left: high molecular weight (HMW) polyubiquitin chains co-purified with GFP tagged-AIRAPL (residues 160-240) were subjected to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LCMS/MS). GFP alone was used as a negative control for binding to ubiquitin. Right: the MS/MS spectrum of the Lys48-linkage GG-containing peptide 43-54 derived from Ub with a precursor ion mass of [M+2H] 2+ 731.0 Da was obtained from cells expressing Flag-AIRAPL. The b/y fragment ions are indicated. (C) Binding of GST-tagged AIRAPL FL and tUIM to Lys48-linked (2-7)-ubiquitin chains was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-ubiquitin antibody. Loading of GST-tagged proteins was determined by Ponceau S staining. (See also Fig. S1) (D) Binding affinity (KD or equilibrium constants) of AIRAPL FL, tUIM and ΔUIM1, WT (wild type) or mutants, for various ubiquitin chain types and lengths measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). For each measurement, His-tagged AIRAPL was immobilized on NiHC1000m chip surface and ubiquitin chains were loaded over the chip. Each measurement was done at least two times and data was analyzed using Scrubber 2 (see also Fig. S2). FL, full-length; tUIM, a construct of AIRAPL comprising tandem UIMs (residues 188-240); ΔUIM1, tUIM construct lacking UIM1; ND, not detected.