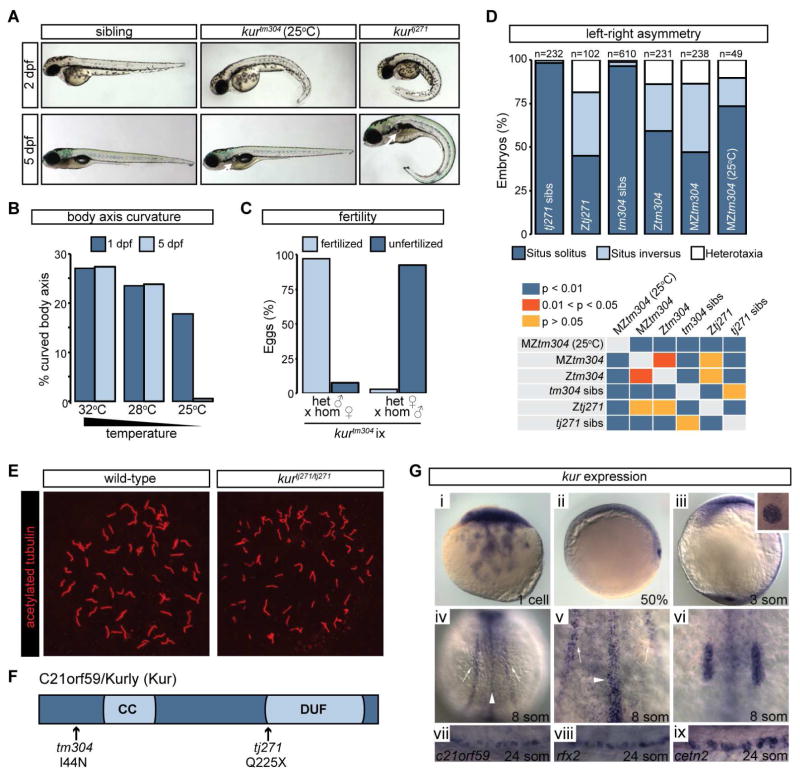
Figure 1. kur Mutants Harbor Mutations in c21orf59 and Exhibit Defects Characteristic of Defective Cilia Motility.
(A) Lateral views of zebrafish sibling control embryos and kurtm304 and kurtj271 mutants at 2 dpf and 5 dpf. At 25°C, kurtm304 mutants exhibit early body axis defects that resolve by 5 dpf whereas kurtj271 mutants do not resolve their body curvatures. Both mutants exhibit kidney cysts (white arrows) but the penetrance is variable in kurtm304/tm304 at 25°C.
(B) Embryos from kur+/tm304 intercrosses were raised at 32°C, 28°C, or 25°C and were scored for body curvature defects at 1 dpf and 5 dpf. Whilst abnormalities were present in around 25% of embryos at 32°C and 28°C, mutants raised at 25°C exhibited fewer incidences of axis curvature at 1 dpf and almost all mutants had recovered at 5 dpf. The total number of embryos examined was 32°C n=292; 28°C n=332; and 25°C n=341. Shown is the average percentage of embryos with curved body axis from 4 biological replicates.
(C) Fertility of kurtm304 adult mutants was assessed by scoring the number of fertilized eggs following homozygous female crosses to heterozygous males and vice versa. Shown is the average percentage of embryos fertilized from 3 biological replicates.
(D) Percentage of embryos showing the indicated situs phenotypes. Embryos were processed by ISH for myl7, ins and fkd2 to mark the heart, pancreas, and liver, respectively, at 2 dpf. Statistical comparison of different genotypes was performed using chi-square analysis with p < 0.05 being considered to report significant differences.
(E) Early somite stage embryos were processed for immunostaining using acetylated alpha-tubulin antibodies to mark the ciliary axoneme. Confocal imaging of KV revealed the presence of cilia in sibling control embryos as well as MZkurtm304 mutants and c21orf59 morphants.
(F) Schematic diagram of C21orf59/Kurly (Kur) protein showing the approximate positions of the predicted coiled coil (CC) domain and the domain of unknown function (DUF). The position and nature of the kurtm304 (I44N) and kurtj271 (Q225X) mutations are shown.
(G) kur expression in zebrafish embryos at the stages indicated. kur is provided maternally at the 1-cell stage (i) followed by expression in the DFCs at 50% epiboly (ii). Expression is observed in KV (iii), pictured here at the 3-somite stage with a close-up of KV in the inset. During somitogenesis, kur is expressed in tissues with motile cilia including the pronephros (white arrows), the floorplate of the neural tube (white arrowheads) and the otic vesicles (iv–vi). Expression in the pronephros at the 24-somite stage overlaps with MCC markers rfx2 and cetn2 (vii–ix).