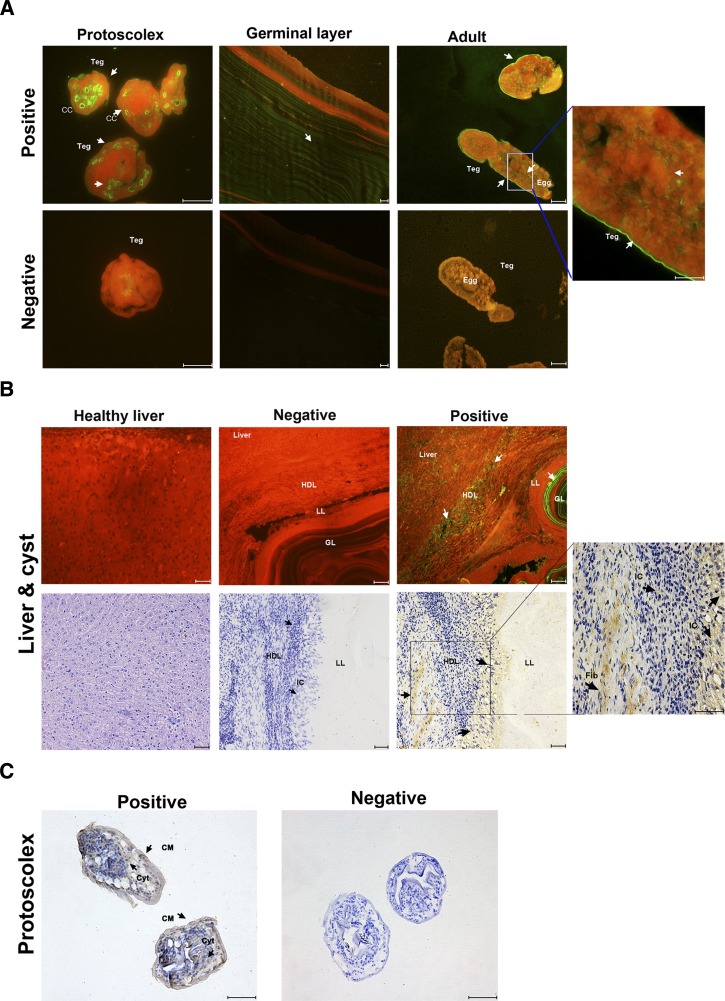
Figure 5.
Immunolocalization of annexin B33 protein of Echinococcus granulosus (Eg-ANX). (A) Immunofluorescence localization of Eg-ANX in different stages of E. granulosus. Eg-ANX in the protoscolex, germinal layer, and adult was immunofluorescently labeled using specific anti-rEg-ANX IgG (positive), or control pre-immune serum (negative), followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. CC = calcareous corpuscle; Teg = tegument. (B) Immunohistochemical localization of Eg-ANX in the host-derived layer and host liver. Eg-ANX in the host liver and host-derived layer was labeled using specific anti-rEg-ANX IgG (positive) or control pre-immune serum (negative), followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG or horseradish peroxidase–conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. The healthy liver was incubated by specific anti-rEg-ANX IgG and stained with hematoxylin–eosin. Fib = fibroblasts; GL = germinal layer; HDL = host-derived layer; IC = inflammatory cells; LL = laminated layer. (C) Eg-ANX localization in cytosol, cellular membrane of protoscoleces. CM = cellular membrane; Cyt = cytosol. Fluorescence-labeled or brown-labeled regions are marked with arrows. Scale bars: 50 μm.