FIG 2.
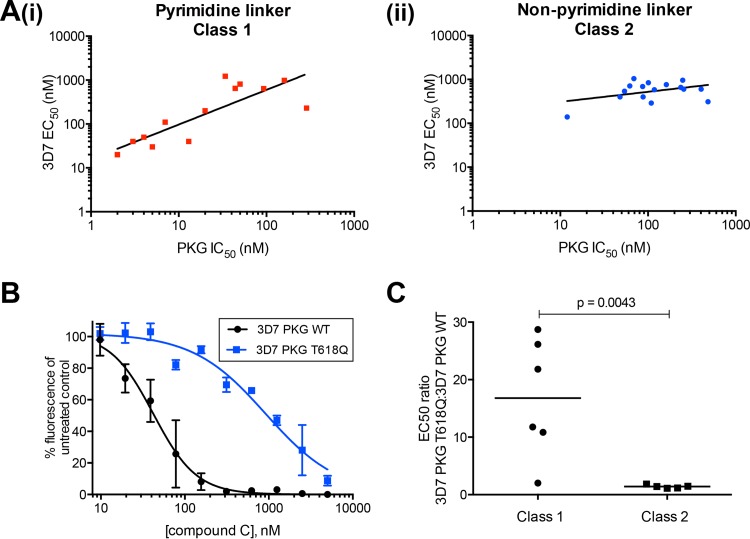
Parasite killing activity of class 1 compounds can be attributed to inhibition of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. (A, panel i) Correlation between P. falciparum EC50 and PKG IC50 for 13 class 1 compounds. The calculated coefficient of determination (r2) value of 0.71 from a linear least-squares regression indicates a good correlation between the two data sets. A P value of 0.0002 indicates a significant relationship between the two measurements. The correlation between P. falciparum EC50 and PKG IC50 for 16 class 2 compounds is also shown (panel ii). An r2 of 0.17 indicates little correlation between the 3D7 EC50 and the PKG IC50 for class 2 compounds. In addition, a P value of 0.114 indicates that there is no significant relationship between the two measures. (B) Parasites expressing a large gatekeeper variant PKG (3D7 PKG T618Q) are insensitive to compound C compared to the sensitivity of WT parasites (3D7 PKG WT). SYBR green assays were used to measure the parasitemia of cultures treated with serial dilutions of compound C for 96 h. The experiment was performed twice; data from a single experiment are shown. The EC50s are 0.923 μM (standard deviation, 0.226) for 3D7 PKG T618Q and 0.042 μM (standard deviation, 0.018) for 3D7 PKG WT parasites. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means of duplicate samples. (C) Mann-Whitney test to compare the ratio of EC50s for 3D7 PKG T618Q/3D7 WT PKG treated with class 1 and class 2 compounds. Horizontal bars show the median values for each class of compounds (16.8 for class 1 and 1.4 for class 2). The calculated P value is 0.0043.