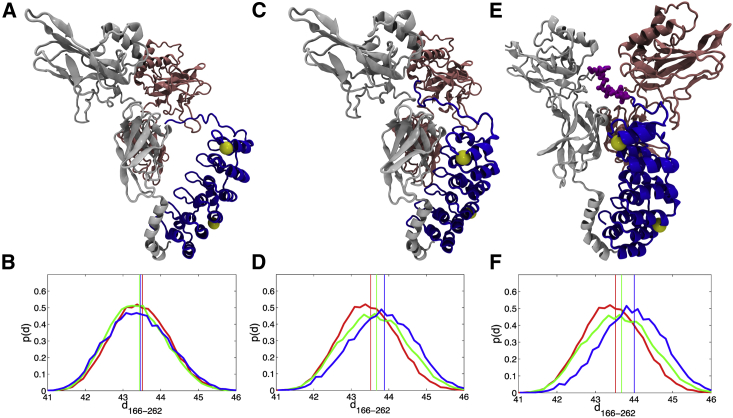
Figure 4.
Representative structures from AWSEM simulations of the NFκB-IκBα complex. IκBα, blue; RelA, light gray; p50 pink. The yellow spheres show the location of the Cβ atoms of residues 166 and 262. (A) Structures with <60% native interfacial contacts formed compared with the crystal structure were selected. (B) The probability distributions of the distance between the Cβ atoms of residues 166 and 262 were calculated from the subset of structures in (A) for free IκBα (red), IκBα bound to dimerization-domain-only NFκB (green), and IκBα bound to full-length NFκB (blue), respectively. The vertical lines indicate the mean values of each distribution; d166–262 was calculated by adding 5 Å to the measured distance between the Cβ atoms of residues 166 and 262. (C) Structures with >60% interfacial contacts formed were selected. (D) The probability distributions of d166–262 for the subset of structures in (C) are plotted in three different colors according to the same scheme as in the previous panel. (E) Structures in which the PEST region (colored magenta) was interacting with RelA were selected. (F) The probability distributions of d166–262 for the subset of structures in (E) are plotted in three different colors according to the same scheme as in the previous panel. The probability distribution for the subset of structures in which the PEST was interacting with the p50 NTD was almost identical to the green curve shown in (D).