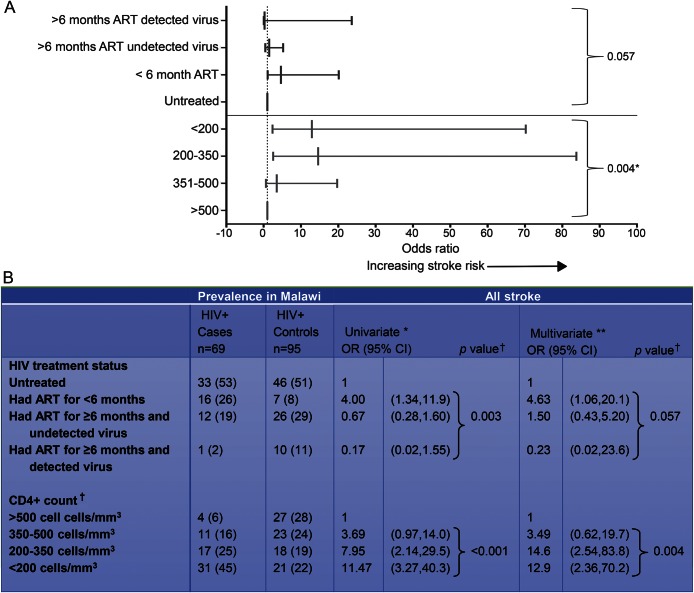
Figure 2. HIV treatment status, viral load, CD4+ count, and stroke risk.
(A) Multivariate analysis of HIV treatment status, CD4+ count, and stroke risk, represented graphically. (B) Univariate and multivariate analysis of HIV treatment status, CD4+ count, and stroke risk. Explores the association of HIV treatment status and stroke risk after adjusting for immunosuppression. *Adjusted for frequency-matched variables: age, sex, and urban location. **Adjusted for hypertension, recent infection, abdominal obesity, HIV treatment status, smoking, current alcohol use, CD4+ T-lymphocyte count, hypercholesterolemia, cannabis use, age, sex, type of housing, and urban location. †A combined p value was calculated using a likelihood ratio test for variables with >2 categories. Data were missing for the following cases and controls: 13 HIV treatment status (including HIV viral load data), 12 CD4+ T-lymphocyte cell count, 2 recent infection, 2 waist-hip ratio, 1 alcohol, 8 pregnant, 1 substance use. Missing observations were included in the analysis by creating missing value categories.