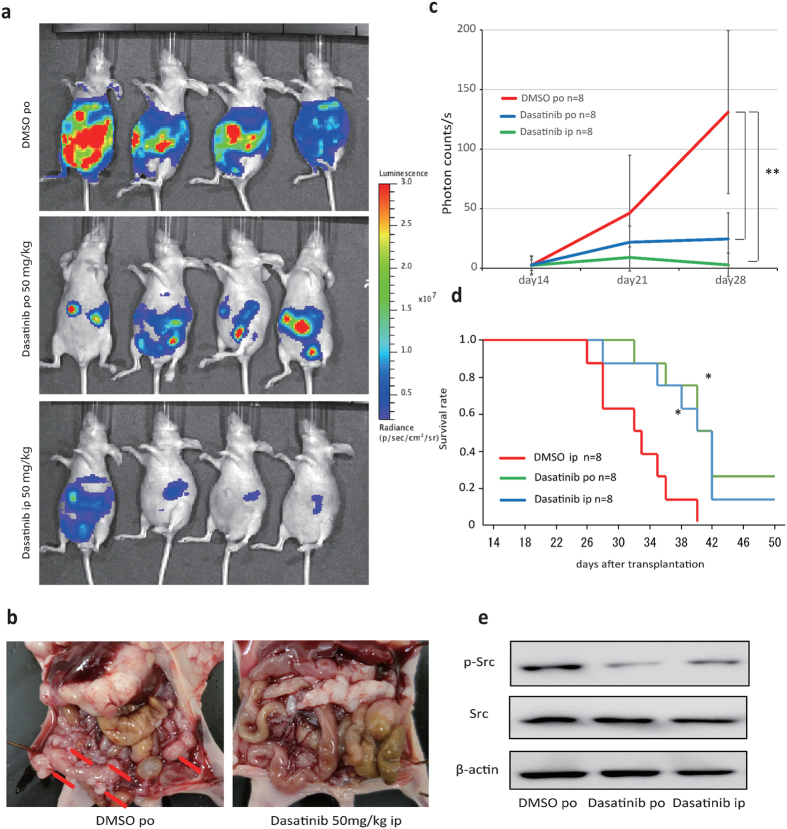
Figure 5. Dasatinib inhibited peritoneal dissemination.
(a) Mice were treated orally and intraperitoneally with dasatinib at 50 mg/(kg·day) or a vehicle control, beginning at day 14 post-transplantation with 58As9Luc cells into the gastric wall. At day 28 post-transplantation, the mice were visualized using the IVIS system. (b) Macroscopic images showed an enlarged peritoneal cavity and metastatic nodules by controlMock3 and shDDR2. Arrowheads show nodules. (c) Normalized bioluminescence photon flux of disseminated peritoneal tumors at day 28 post-transplantation, as visualized by the IVIS system. The control and orally plus intraperitoneally administered dasatinib groups each contained n = 8 mice. **p < 0.01. (d) Survival curves showed that survival rate in dasatinib-treated mice was significantly higher (*p < 0.05) than that in control mice. (e) Src and Src phosphorylation, as measured by immunoblotting.