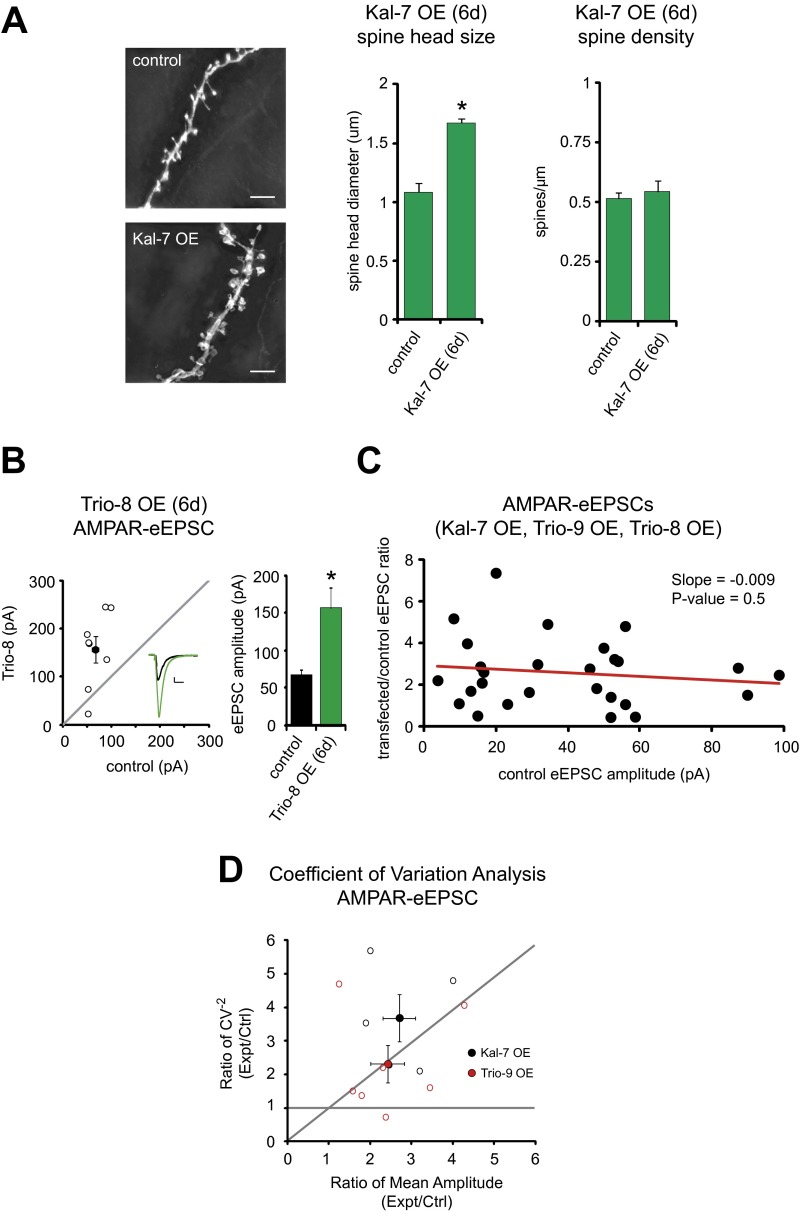
Fig. S1.
Kalirin/Trio OE: effects on spine morphology, phenotype dependence on stimulation strength, and effects on quantal content. (A) Bar graphs showing mean ± SEM spine head diameter (Left) and spine density (Right) of control and Kal-7 OE CA1 pyramidal neurons (control, n = 6 neurons; Kal-7 OE, n = 6 neurons; *P = 0.005). Representative images of dendritic spines of control and Kal-7 OE CA1 pyramidal neurons are shown on the left. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (B) Scatterplot showing amplitudes of AMPAR- and NMDAR-eEPSCs for single pairs of control and Trio-8 transfected neurons (open circles). Filled circles indicate mean ± SEM. The bar graph shows mean ± SEM AMPAR-eEPSC amplitude for control and Trio-8 OE neurons (n = 8 pairs; *P = 0.01). (Inset) Sample current traces from control (black) and transfected (green) neurons. (Scale bars: 20 ms, 20 pA.) (C) Scatterplot showing transfected/control AMPAR-eEPSC amplitude ratio vs. control AMPAR-eEPSC amplitude for single pairs of control and Kal-7, Trio-9, or Trio-8 transfected neurons. Linear regression analysis was performed on the data (red line). (D) Coefficient of variation analysis of simultaneously recorded pairs of control/Kal-7 OE and control/Trio-9 OE neurons (open circles). CV−2 is graphed against the ratio of mean amplitude within each pair. Results along the horizontal line are consistent with changes in quantal size (q); results along the identity (45°) line are consistent with changes in quantal content (N × Pr). Analysis of AMPAR responses indicates that the increase in amplitude produced by Kal-7 and Trio-9 is due to an increase in quantal content (Kal-7 OE, n = 5 pairs; Trio-9, n = 7 pairs).