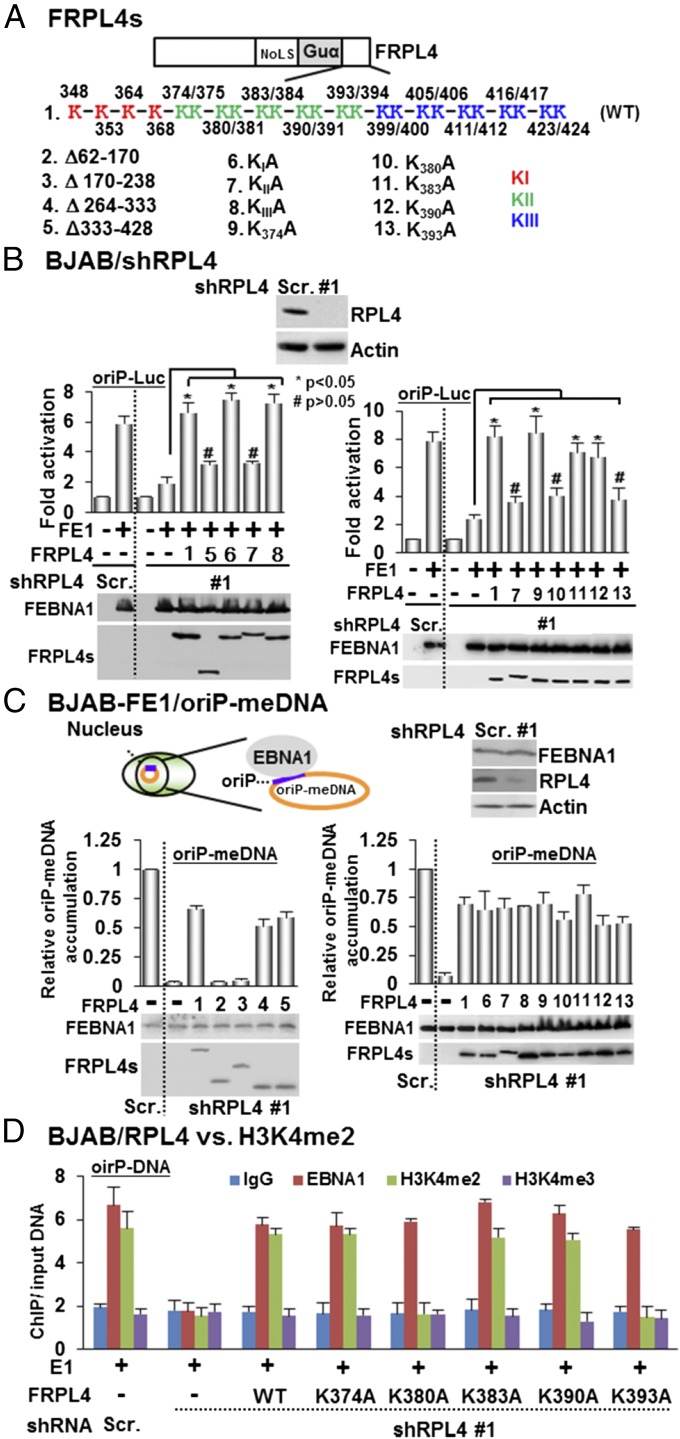
Fig. 4.
The N terminus of RPL4 is involved in EBNA1 and oriP-dependent episomal DNA maintenance, whereas the C-terminal K383 and K390 have a specific role in EBNA1 and oriP-mediated transcription. (A) Schematic diagrams of FRPL4 and its deletion or point mutants. (B) RPL4 was depleted in BJAB cells by shRPL4 #1. FLAG-tagged EBNA1 and oriP luciferase reporter plasmids were cotrasfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type RPL4 or its deletion and point mutants. shRPL4 knockdown greatly reduced EBNA1 activation of oriP luciferase. Wild-type RPL4 rescued RPL4 shRNA knockdown effect and restored EBNA1 activation of oriP luciferase. Protein expression was determined by Western blotting. *P < 0.05; #P > 0.05 versus control. (C) shRPL4 was used to deplete PRL4 in BJAB cells stably expressing FEBNA1 and maintain mini-EBV episome DNA (oriP-meDNA) (28). qPCR was used to determine the mini-EBV episome copy number. RPL4 knockdown greatly reduced the mini-EBV episome copy number, whereas FLAG tagged wild-type RPL4 rescue restored the mini-EBV episome copy number. RPL4 deletion and point mutants were also tested for their effects. GAPDH genomic DNA was used to normalize the qPCR. oriP DNA in Scramble control cells was set to 1. The FEBNA1 and FRPL4 expressions were determined by Western blotting. (D) BJAB cells depleted for RBL4 expression by shRPL4 #1 or control cells were transfected with EBNA1 and oriP plasmids. Wild-type RPL4 or RPL4 lysine mutants were also cotransfected to rescue RPL4 knockdown. Antibodies against EBNA1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, or control were used in ChIP assays to assess the oriP EBNA1 binding and histone modifications. oriP fold enrichment over input DNA was determined by qPCR.