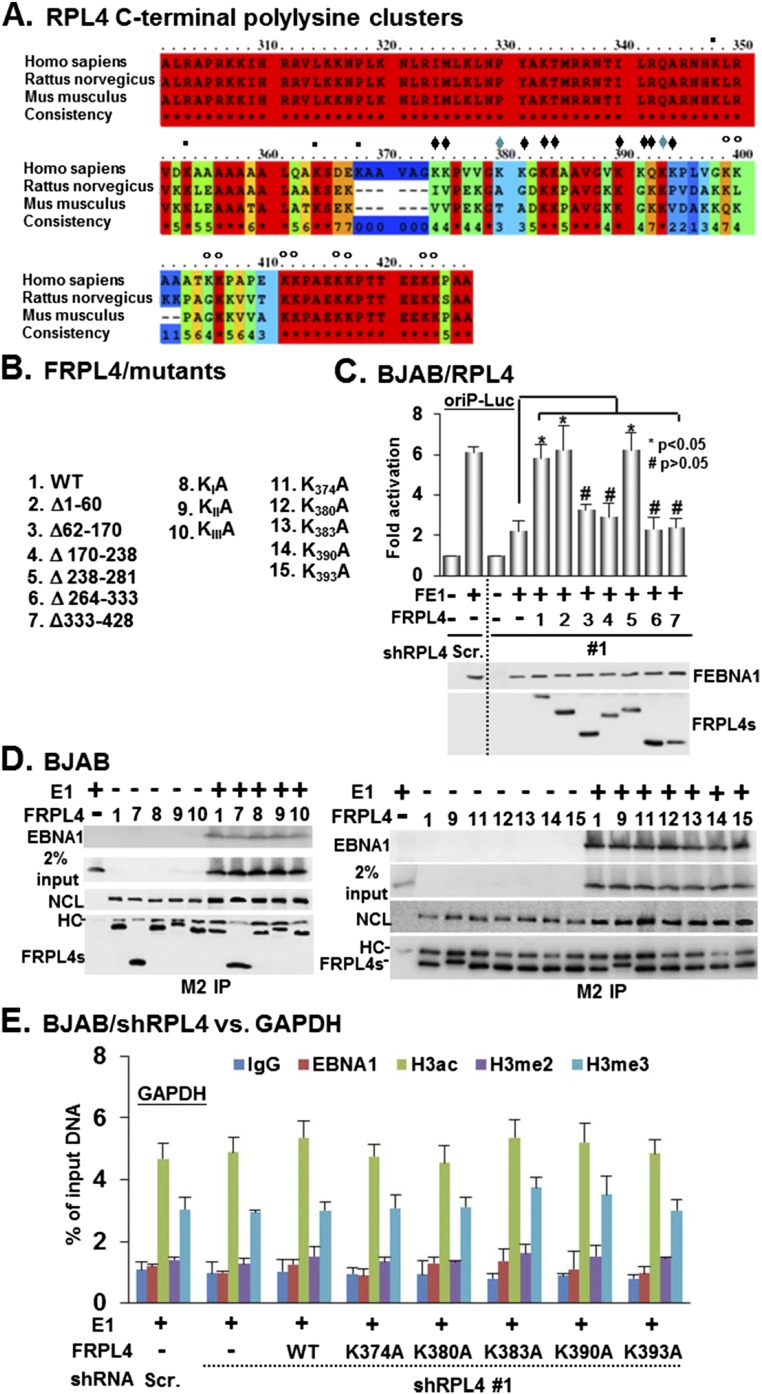
Fig. S6.
RPL4 C terminus is not required for either EBNA1 or NCL association. (A) Sequence alignments of RPL4 C terminus from human, rat, and mice were shown. The polylysine clusters were indicated by ▪KI, ♦KII, and °KIII, respectively. (B) The schematic diagrams of FRPL4 and its mutant derivatives are shown. (C) BJAB/shRPL4 #1 cells were used to perform transfection-mediated complementation of EBNA1/oriP-Luc–dependent transcription using the indicated FRPL4 plasmids. Protein expression and actin internal control were determined by Western blot. *P < 0.05; #P > 0.05 versus control. (D) BJAB cells were cotransfected with the plasmids of EBNA1 (E1) and FRPL4 or its mutant derivatives and subjected to a M2 IP protocol. FRPL4-precipitated EBNA1 or NCL was determined by Western blot. We used 2% input of EBNA1 as a loading control. (E) RPL4 depletion did not affect the enrichment of histone modifications at the GAPDH promoter. BJAB/shRPL4 #1 or BJAB/Scr. cells were cotransfected with EBNA1 and the indicated FRPL4 plasmids. Each transfectant was subjected to ChIP assays using IgG or antibodies for EBNA1, H3ac, H3K4me2, and H3K4me3. The amount of ChIPed GAPDH promoter DNA was quantified by qPCR and determined as % of input DNA.