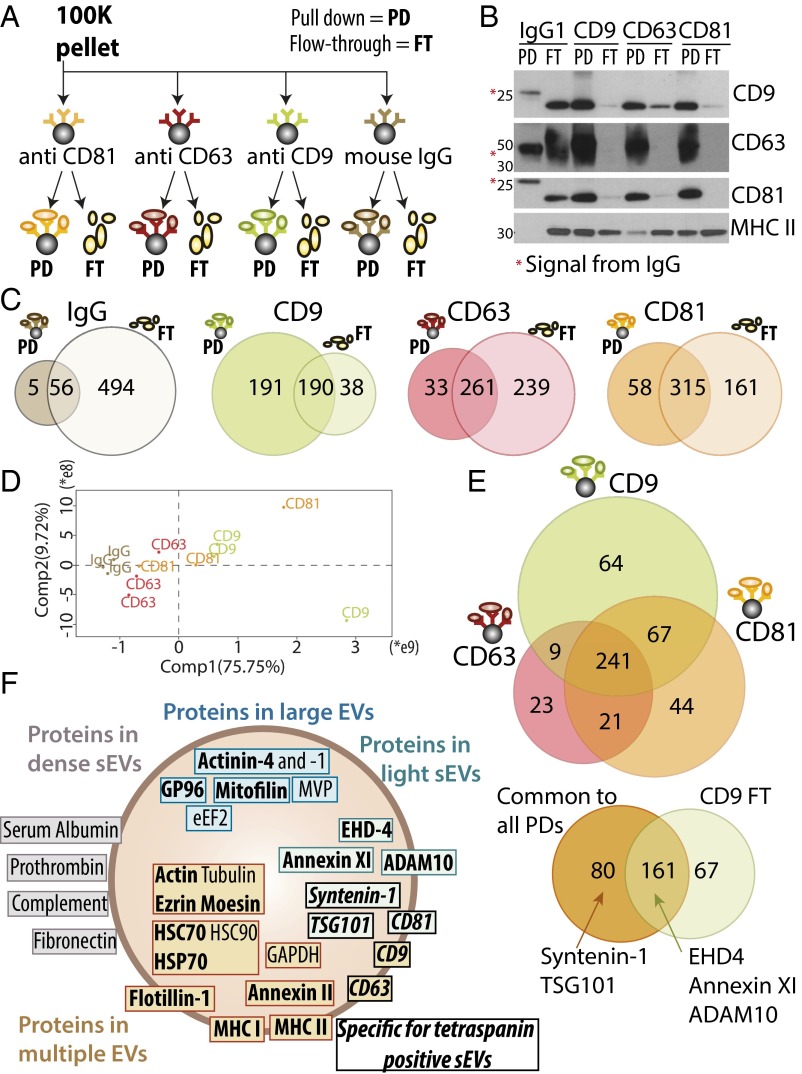
Fig. 5.
Qualitative and quantitative proteomic analyses of sEVs immuno-isolated by CD9, CD63, or CD81-specific antibodies evidence additional sEV subpopulations. (A) The crude DC-derived 100K pellet was subjected to parallel immuno-isolation with beads coupled to irrelevant murine IgG, or antibodies against CD9, CD63, or CD81. PD vesicles and nonpulled down materials remaining in the FT were subjected to subsequent comparative analysis. (B) Equal volumes of materials from each PD and FT (the latter after concentration by ultracentrifugation) were loaded on a gel for Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for CD9, CD63, CD81, or MHC class II. All beads precipitated efficiently vesicles bearing the targeted protein. Note the remaining presence of CD9+ and CD81+ materials in the FT of CD63-beads, and of MHC II+ materials in the FT of all immuno-isolations, showing the existence of tetraspanin-negative sEVs. *Nonspecific signal from the immunoglobulins’ heavy (50 kDa, CD63 blot) or light (25 kDa, CD9 and CD81 blots) chains used for immuno-precipitation. (C) PD and FT obtained as shown in A and B were analyzed by label-free LC-MS/MS. Venn diagrams represent the number of proteins detected in each sample with minimum three peptides in each of three independent replicates, comparing PD and FT obtained from each antibody after exclusion of the 61 proteins present in the PD of irrelevant IgG. (D) Quantitative PCA shows that the CD63-PD are distinct from the CD81- and CD9-PD. (E) Venn diagram showing proteins identified in PD obtained from the three antitetraspanin antibodies (Upper), and distribution of the 241 proteins common to the CD9-, CD63-, and CD81-PD, compared with the FT of CD9 (Lower). Position of sEV-specific proteins is indicated. (F) Assignment of the proteins analyzed here, and previously described as canonical exosome markers, to the different types of EVs, as demonstrated by Western blotting (bold) or by the quantitative proteomic comparison. EVs are schematized as a lipid bilayer (thick brown circle) enclosing cytosol (light background). Brown: proteins shared by several types of EVs. Green: proteins specifically enriched in F3-100K (i.e., the light sEVs), including those specific of the tetraspanin-enriched endosome-derived exosomes (italic font), and those ubiquitously present in all sEVs. Gray: proteins coisolated with the small EVs (100K pellets) but in EVs of higher density (F5-100K). Blue: proteins specifically enriched in large and medium-sized EVs.