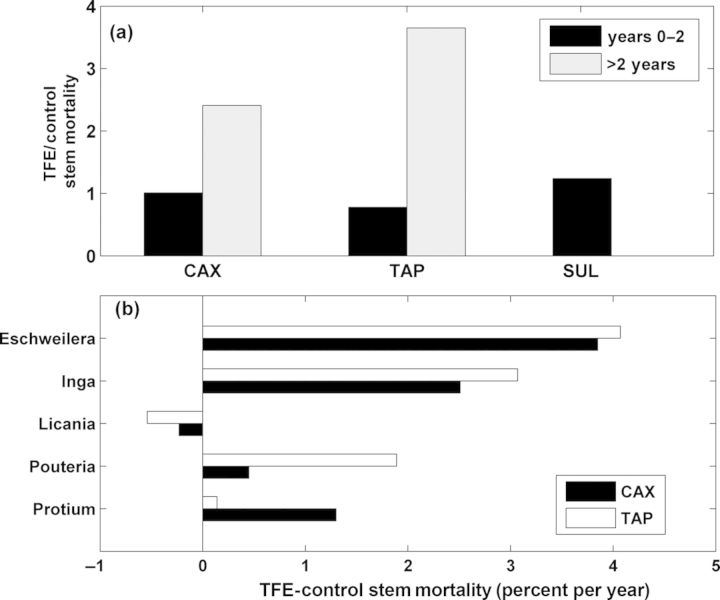
Figure 2.
(a) Tree (more than 10 centimeters [cm] diameter at breast height [dbh]) mortality responses in three ecosystem-scale throughfall exclusion (TFE) experiments in tropical rain forest, Caxiuanã National Forest (CAX), Tapajós National Forest (TAP), and SUL (Sulawesi Throughfall Exclusion Experiment; dimensionless quotient of TFE/control). The data are presented for years 0–2 and years 2–7 of TFE treatment (Nepstad et al. 2007, da Costa et al. 2010); the SUL experiment was terminated after 2 years (Moser et al. 2014). The 1-hectare [ha] TFE treatments at CAX and TAP were not replicated because of their large size (Fisher et al. 2007, Nepstad et al. 2007). The TFE design at SUL was three smaller (0.16-ha) plots located close to each other; treatment replication yielded an uncertainty of 1.3% to the mortality response (TFE/stem mortality). Background mortality at CAX was 1.2% ± 0.2 SE (n = 6; da Costa et al. 2010), that at TAP was 2.4% (n = 1; Brando et al. 2008), and that at SUL was 2.1% ±0.4 SE (n = 3, Moser et al. 2014). (b) The absolute difference in tree (more than 10 cm dbh) mortality response to TFE at CAX and TAP for the five most common genera at CAX. The five most common genera at TAP were Eschweilera, Protium, Coussaria, Erisma, and Sclerolobium.