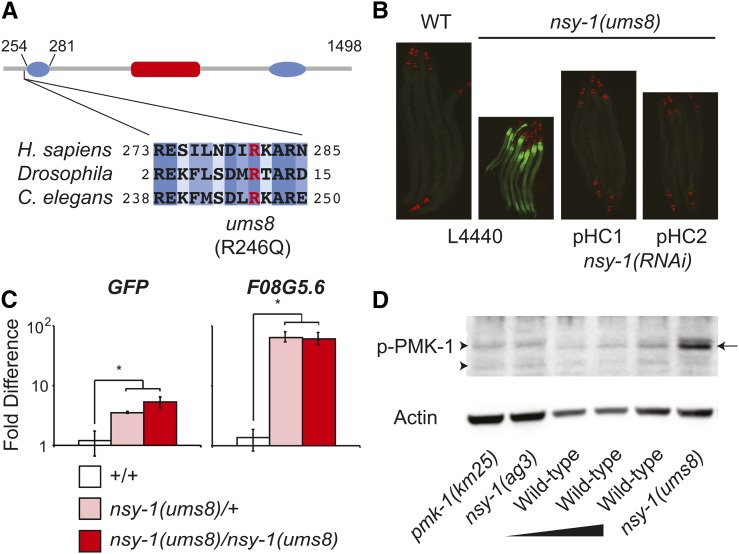
Figure 2.
The nsy-1(ums8) allele encodes a gain-of-function mutation in nsy-1. (A) The putative domain architecture of NSY-1, based on homology to mammalian ASK1, is presented. This schematic was adapted from Bunkoczi et al. (2007). The putative location of the central serine-threonine kinase domain, and two coiled-coil domains in the N and C termini are shown in red and blue, respectively. The boundary of the N-terminal negative regulatory domain relative to the NSY-1 protein is presented above the diagram. The Arg that was mutated to Gln in the ums8 strain (R246Q) is highlighted in red. Amino acid sequence alignment of human ASK1, Drosophila Pk92B (the ASK1 homolog) and C. elegans NSY-1 demonstrates that the ums8 mutation is located in a strongly conserved region. Dark blue shading indicates identical amino acids, with progressive lighter blue shading indicating the level of similarity in amino acid class as determined by the software ClustalW2. (B) Wild-type (WT) and nsy-1(ums8) animals were exposed to the feeding RNAi bacteria strain transformed with the control vector (L4440), or with two separate RNAi constructs (pHC1 and pHC2) that target different areas of coding region in the nsy-1 gene and photographed. Green is F08G5.6::GFP induction and red is myo-2::mCherry, which was used as the co-injection marker. (C) The expression of the indicated genes was determined using qRT-PCR in wild-type (+/+), nsy-1(ums8)/+ heterozygotes, and nsy-1(ums8)/nsy-1(ums8) homozygotes. F08G5.6::GFP was used as the wild-type strain. Data are the average of three replicates, each normalized to a control gene with error bars representing SEM, and are presented as the value relative to the average expression of the indicated gene in wild-type animals. * equals P < 0.05. There was no statistical difference in the levels of induction between the heterozygous and homozygous samples for either gene. For additional genes tested, see Figure S1A. (D) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from L4 larval stage animals of the indicated genotype using antibodies that recognize the doubly phosphorylated TGY motif of PMK-1 (p-PMK-1) and actin. Thirty μg of nsy-1(ums8), pmk-1(km25) and nsy-1(ag3) total protein were loaded on the gel alongside a dilution series of wild-type template [15 μg, 20 μg, and 30 μg of total protein (left to right)] to control for the ability of the p-PMK-1 antibody to detect different concentrations of substrate. The arrow on the right highlights the PMK-1 band, which is absent in the pmk-1(km25) and nsy-1(ag3) mutants. The arrowheads on the left point to nonspecific bands. Data are representative of two biological replicates.