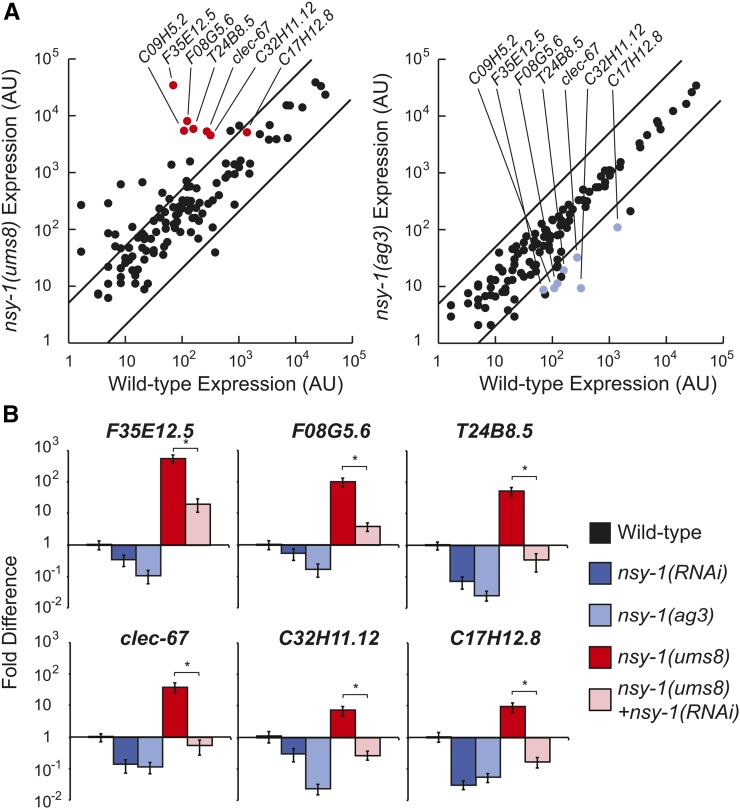
Figure 3.
p38 MAPK-dependent putative immune effectors are constitutively activated in the nsy-1(ums8) mutant. (A) A scatter plot compares the expression of 118 C. elegans genes, which were analyzed using nanoString nCounter gene expression system in wild-type, nsy-1(ums8) and nsy-1(ag3) animals. Data are the average of two replicates for nsy-1(ums8), and nsy-1(ag3), and are from one sample for wild-type. The expression of each gene was normalized to the geometric mean of the expression of three control genes. Genes that are outside the two parallel lines on each graph are differentially regulated more than fivefold from the expression in wild-type animals. Genes that are previously characterized targets of the p38 MAPK PMK-1, and were strongly differentially regulated in this experiment, are highlighted. See Table S1 for the expression levels of all the genes. (B) qRT-PCR was used to study the expression of six putative immune effectors in RNAi-treated, mixed-stage animals of the indicated genotypes. All animals were grown on the RNAi bacteria feeder strain HT115 expressing the empty vector L4440, except for the two indicated samples that were exposed to bacteria expressing the nsy-1(RNAi) construct. The location on the scatter plots of these genes is indicated in (A) with red (left) and blue (right) dots. Data are the average of three replicates, each normalized to a control gene with error bars representing SEM, and are presented as the value relative to the average expression of the indicated gene in wild-type animals. * equals P < 0.05.