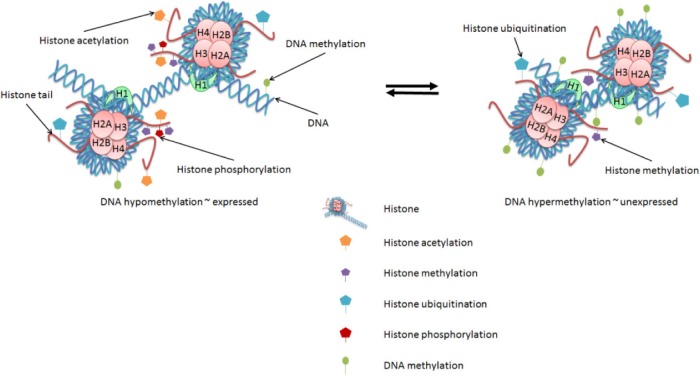
Figure 1.
Chromatin modifications affect gene expression. Changes in epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, each contribute to the regulation of gene expression. DNA methylation in the promoter regions of genes is generally associated with decreased gene expression. Histone modifications can be either activating or repressive. Histone acetylation and phosphorylation are generally associated with active genes; histone methylation and ubiquitination arrangements are associated with either active or repressed genes.