Figure 6.
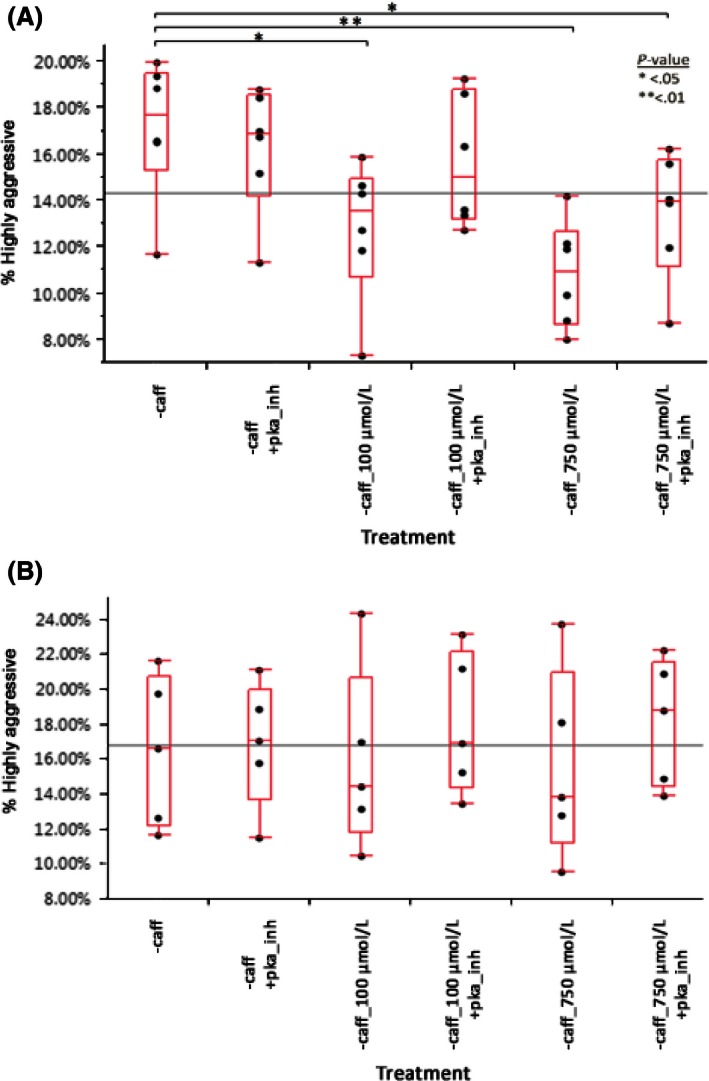
(A) Noncaffeine drinkers’ mononuclear phagocytes show significant reductions in aggressiveness when treated with either 100 μmol/L (P = 0.0314) or 750 μmol/L caffeine (P = 0.0037). Addition of PKA inhibitor reversed this reduction for 100 μmol/L caffeine, but not totally for 750 μmol/L caffeine (P = 0.0117). Data generated using a matched paired t‐test. n = 6. (B) Caffeine drinkers’ mononuclear phagocytes show no sensitivity to caffeine at 100 or 750 μmol/L concentrations. PKA inhibitor also had no effect on these cells’ aggressiveness. Data generated using a matched paired t‐test. n = 5.
