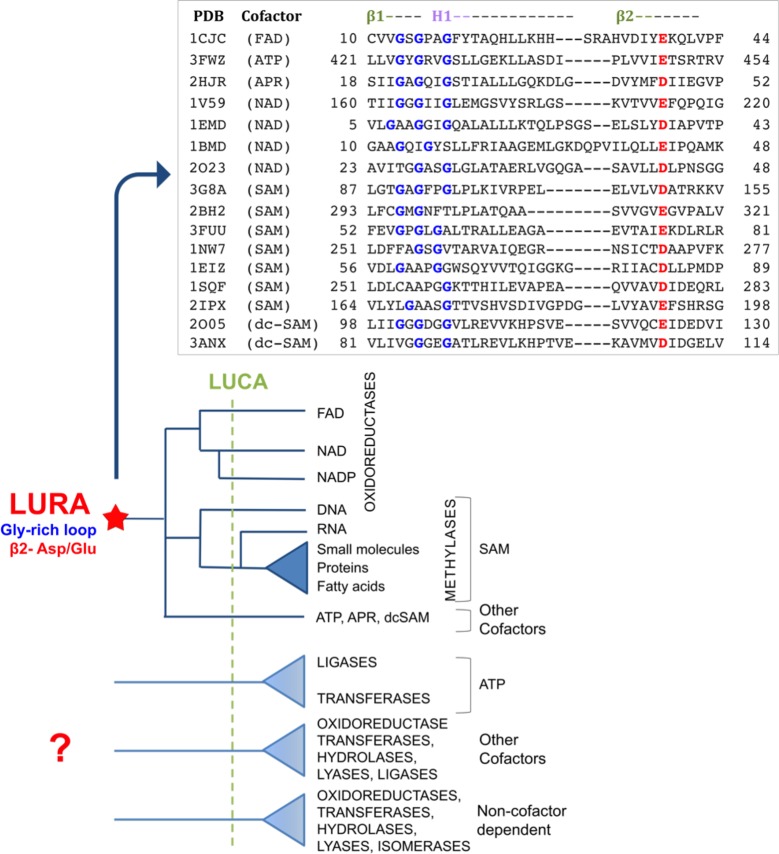
Fig 6. Manual alignment of the β1-H1-β2 segments of representative Rossmann-fold enzymes that possess the canonical motif and a schematic evolutionary tree of the Rossmann fold.
Shown are representatives from the four major classes that seem to have diverged from a common ancestor carrying the β2-Asp/Glu motif (Fig 1). The ribose-binding β2-Asp/Glu is in red. As previously noted [5,33], the motif GxGxxG (in blue) is present in almost all the NAD/FAD enzymes, as well as in enzymes utilizing other phosphate-containing cofactors (ATP, AMP, and adenosine-5-diphosphoribose [APR]). In SAM (or dc-SAM) utilizing enzymes, the Gly-rich motif is blurred as expected for a cofactor that does not contain a phosphate group. The schematic tree originates from a presumed last universal Rossmann ancestor (LURA), and it is based on Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers and CATH classification of LUCA’s enzymes (S1 Table). The star designates the presumed common Rossmann ancestor that includes the ribose-(Asp/Glu-β2) and the Gly-rich motifs.