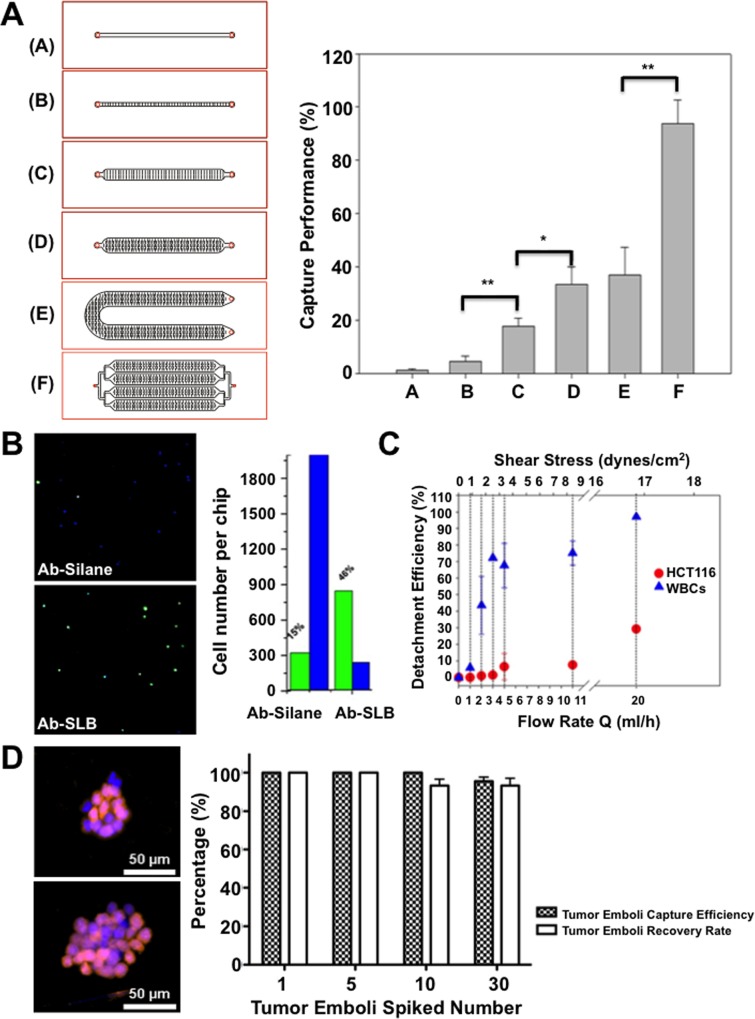
Fig 2. Capture performance and purification by Ab-SLB coated microfluidics.
(A) The geometry and patterns of 6 different microfluidic channel designs (left) and the capture efficiency of these microfluidic platforms (right) as defined by dividing captured cells over total spiked cells. (B) The cropped fluorescent images (5.5 mm x 5.5mm) inside the flow channel and the enumeration of HCT116 (green) and WBCs (blue) on Ab-SLB or Ab-silane coated Type E chips. (C) Cell detachment efficiency (%, Y-Axis) vs. flow rates (ml/h, lower X-axis) and the corresponding shear stress (upper X-axis). Flow rates are generally maintained below 4 ml/h to avoid any potential loss of captured CTCs. (D) Highly CTM capture and recovery efficiency of the Ab-SLB coated chip. The capture efficiency and recovery rate of HCT116-RFP generated tumor microemboli were showed in right panel. The released HCT116-RFP CTC clusters with DAPI staining were showed in left panel. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01.