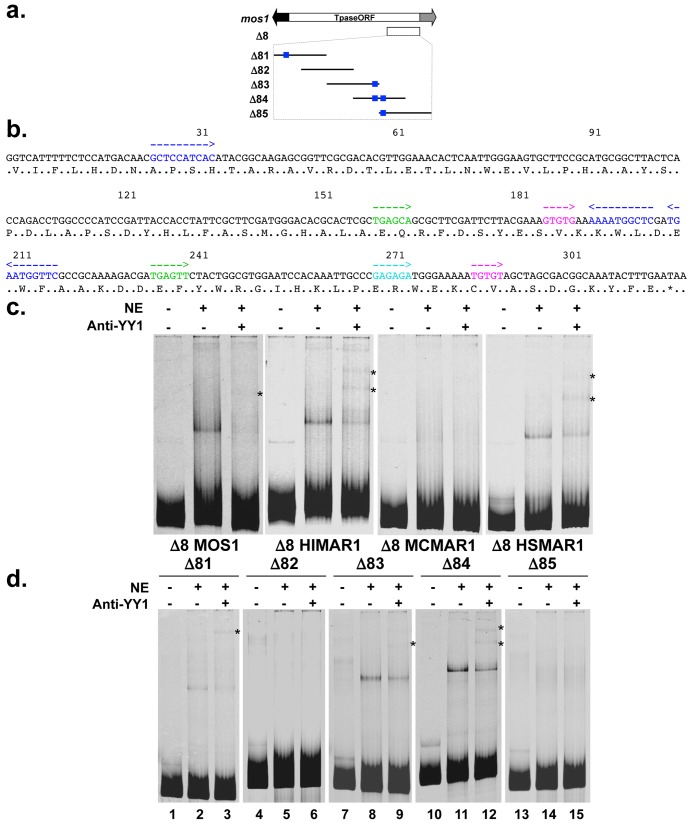
Fig 6. Characterization of the YY1 binding sites within the Δ8 segments.
(a) Schematic representation of the Mos1 transposon and its 10 deletion derivatives used to define a minimal silencer (Δ8 and Δ81 to Δ89). Δ8 spanned from positions 903 to 1212 of the Mos1 sequence. Five derivatives of ~100 bp were tiled over ~50 bp (Δ81 to Δ85). Blank rectangle: Mos1 transposase (Tpase ORF). Black arrow: 5’ ITR fused to the 5’ UTR. Grey arrow: 3’ UTR fused to the 3’ ITR. (b) Nucleic acid sequence of the Δ8-MOS1 segment and putative TF binding sites frequently found within PRE in drosophila. Blue: YY1, red: NRSF, green: Zeste, pink: GAGA factor, turquoise: GTGT factor. Arrows indicate their orientation. The amino acid sequence of the C-terminal region of MOS1 is indicated using the one-letter code. (c) DNA binding activity of the YY1 factor to the Δ8-MOS1, Δ8-HIMAR1, Δ8-MCMAR1, and Δ8-HSMAR1 segments. HeLa cells nuclear extracts were incubated with the ATTO-labelled Δ8 segments of the four transposases and the DNA-protein complexes were visualized by EMSA photography. Specificity was assayed using an anti-YY1 serum and super-shifted YY1/Δ8 complexes (one or two bands) are indicated by an asterisk. The content of each sample is shown above each lane: NE: nuclear extract, Anti-YY1: anti-YY1 serum. (d) Detection of YY1 binding sites within the Δ81 to Δ85 segments. The specificity of the shifted complex observed in lane 2, 8 and 11 was verified in lane 3, 9 and 12 in which the anti-YY1 serum allows obtaining super-shifted complexes (indicated by *). All these experiments were done in triplicate and representative pictures are shown.