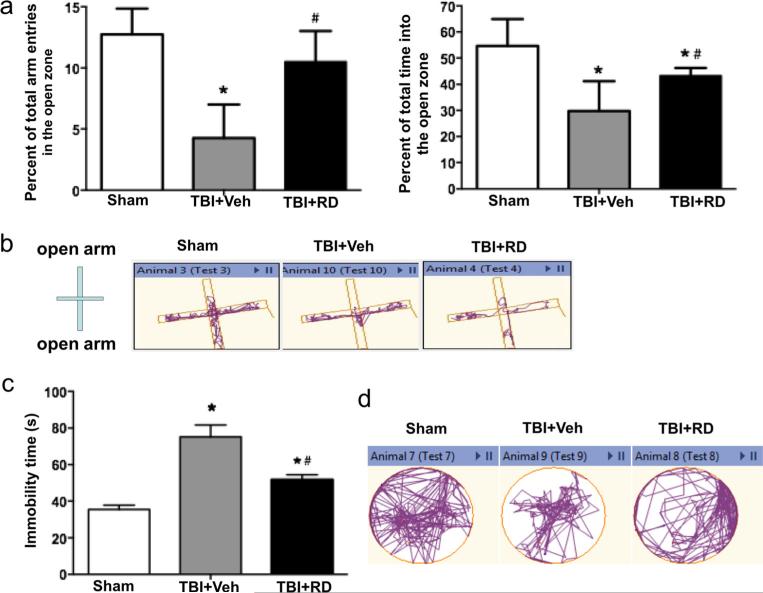
Fig. 2.
Effects of Rhizoma drynariae (RD) on anxiety- and depression-like behavior in rats subjected to CCI. Anxiety- and depression-like behavior were assessed by the elevated-plus maze (a, b) and the forced swim test (c, d), respectively, on day 21 after CCI. a The total number of entries into the open arms and the total time spent in the open arms were significantly less in R. drynariae-treated rats than in vehicle-treated rats over the duration of the test. b Representative activity traces from sham, vehicle-, and R. drynariae-treated rats in the elevated-plus maze test. c R. drynariae treatment decreased the immobility time in the forced swim test compared to that of vehicle-treated rats. d Representative swim paths of sham, vehicle-, and R. drynariae-treated rats in the forced swim test. Values are mean±SD; n=6 rats/group; *p<0.05 vs. sham group, #p<0.05 vs. vehicle group