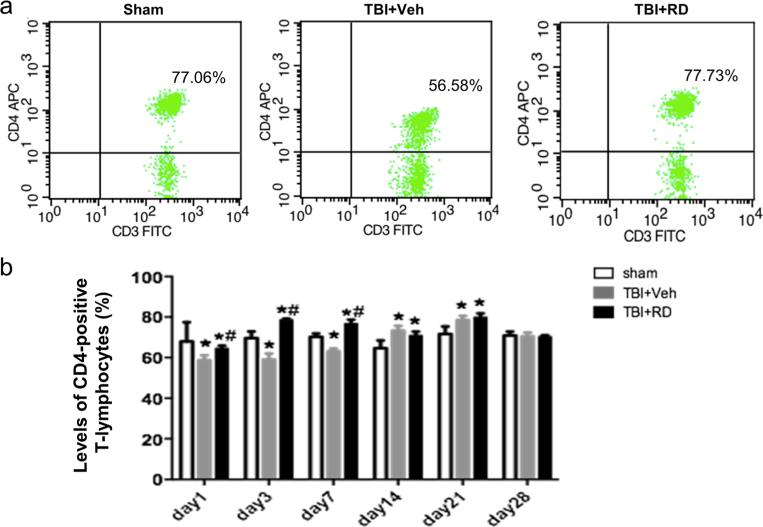
Fig. 5.
Effects of Rhizoma drynariae (RD) on CD4-positive T lymphocytes in the blood of rats subjected to CCI. CD4-positive T lymphocytes were measured in blood by flow cytometry on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 after CCI. (a) Representative flow cytometric dot plots show the percentage of CD4-positive T lymphocytes in sham, vehicle- and R. drynariae-treated rats on day 3 after CCI. b Histograms show that the percentage of CD4-positive T lymphocytes was significantly lower in the vehicle-treated group than in the sham group on days 1, 3, and 7 after CCI and that R. drynariae treatment reversed these decreases. The percentage of CD4-positive T lymphocytes was significantly higher in the vehicle- and R. drynariae-treated groups than in the sham group on days 14 and 21 after CCI but did not differ between the two treatment groups. Values are mean±SD; n=6 rats/group; *p<0.05 vs. sham group, #p<0.05 vs. vehicle group