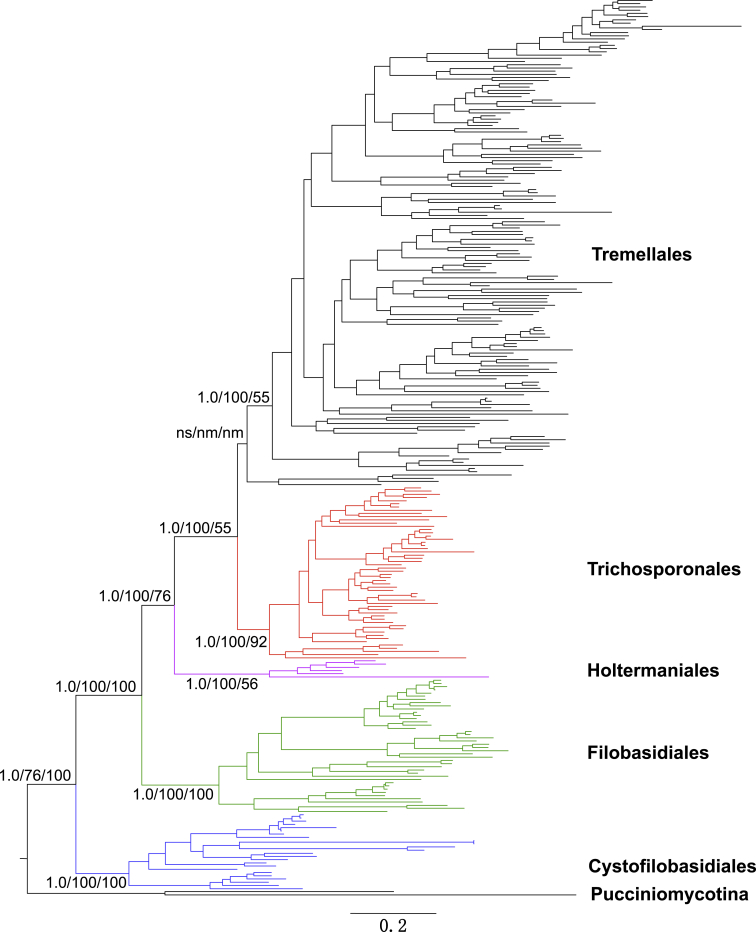
Fig. 1.
An outline of the phylogeny of tremellomycetous yeasts and dimorphic taxa inferred from a seven-gene data set including sequences of three rDNA genes, RPB1, RPB2, TEF1 and CYTB. The tree backbone is constructed using Bayesian analysis. Branch lengths are scaled in terms of expected numbers of nucleotide substitutions per site. The Bayesian posterior probabilities (PP) and bootstrap percentages (BP) of maximum likelihood and neighbour-joining analyses from 1 000 replicates are shown respectively from left to right on the deep and major branches resolved. Note: ns, not supported (PP < 0.9 or BP < 50 %); nm, not monophyletic.