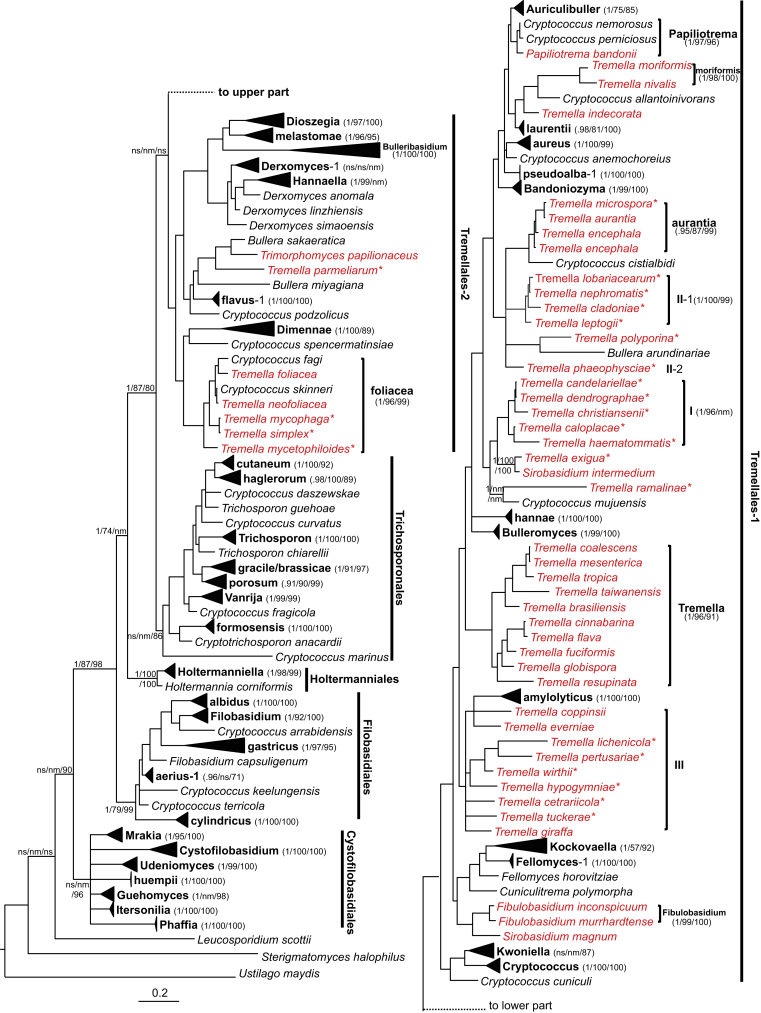
Fig. 7.
Phylogeny of tremellomycetous yeasts and dimorphic taxa based on 5.8S and LSU D1/D2 rDNA sequences from strains employed in this study and 26 more Tremella species employed in Millanes et al. (2011). The tree backbone is constructed using Bayesian analysis. The Bayesian posterior probabilities (PP) and bootstrap percentages (BP) of maximum likelihood and neighbour-joining analyses from 1 000 replicates are shown respectively from left to right on the deep and major branches and in brackets following the clades resolved. The species names in red represent fruiting-body forming taxa and those with a star superscript indicate that the sequences are from herbarium specimens of lichen-inhabiting species. Note: nm, not monophyletic; ns, not supported (PP < 0.9 or BP < 50 %).