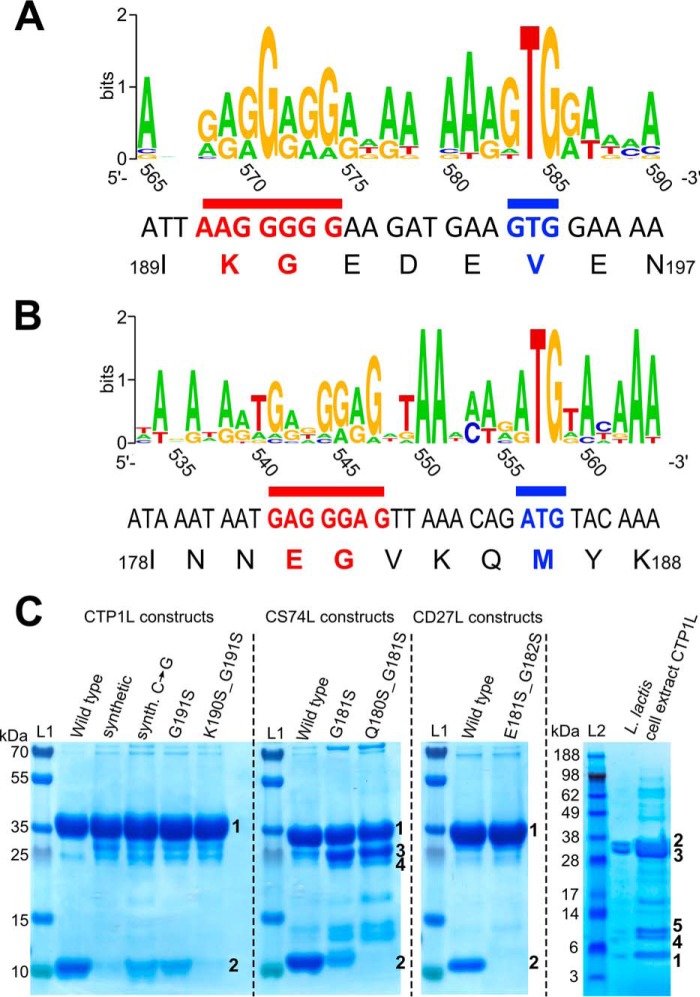
FIGURE 4.
A, sequence logo created with Weblogo (49) showing the linker region of CTP1L with nucleotides numbered according to the CTP1L nucleotide sequence based on a sequence alignment of CTP1L-related lysins as presented by Dunne et al. (16). The Shine-Dalgarno region is underlined in red, and the start codon is underlined in blue. B, sequence logo showing the linker region of CD27L with nucleotides numbered according to the CD27L nucleotide sequence. The Shine-Dalgarno region is underlined in red, and the start codon is underlined in blue. C, SDS-PAGE shows the effect of mutations in the ribosomal binding site of endolysins CTP1L, CD27L, and CS74L on the expression of the truncated CBD. The wild-type protein produced from the wild-type bacteriophage nucleotide sequence is compared with a codon-optimized (synthetic) gene for CTP1L. A silent mutation of CTP1L is shown (Synth C → G), which restores the RBS region from the codon-optimized gene sequence to the wild-type sequence. Mutants of the glycine (GGG) that forms part of the RBS in CTP1L and CS74L to serine (TCT) do not abolish expression, but the RBSKO mutations (K190S/G191S for CTP1L, E180S/G181S for CS74L, and E181S/G182S for CD27L) reduce expression of the truncated domain drastically. Lane L, marker. Bands marked as 1 have been identified as full-length protein; bands marked as 2 have been identified to contain an N-terminal methionine and are the product of secondary translation. Bands marked with 3 and 4 occur in CS74L constructs where the secondary translation site has been compromised, and these bands have been identified by peptide fingerprinting as degradation products of full-length CS74L. The far right panel shows pooled concentrated eluates of N-terminally His-tagged CTP1L expressed in L. lactis. Excision of bands and analysis by tryptic digest and MALDI-ToF-MS showed that this band 1 contained 100% of the peptides expected from the translation product of the alternative start site (Met-195) with no incidence of Val-195. The larger bands (2 and 3) contained peptides of the full-length sequence, including Val-195, whereas bands 4 and 5 both contained peptides matching the secondary translation product in addition to selected peptides from the full-length lysin sequence.