FIGURE 1.
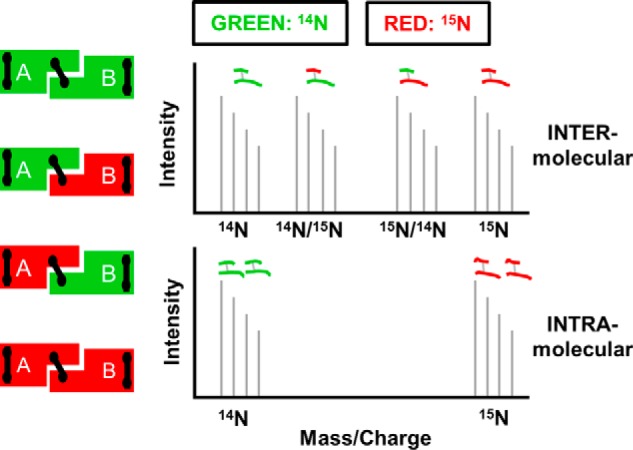
Principle behind isotope-assisted cross-linking. Recombinant proteins produced with either 14N amino acids (green) or 15N amino acids (red) are mixed at a 1:1 ratio under denaturing conditions and allowed to reassemble, resulting in the four combinations on the left. Proteins are locked into position by cross-linking and digested with trypsin. Intermolecular cross-links result in four mass peaks as shown in the top panel, whereas intramolecular cross-links result in two mass peaks shown in the bottom panel.
