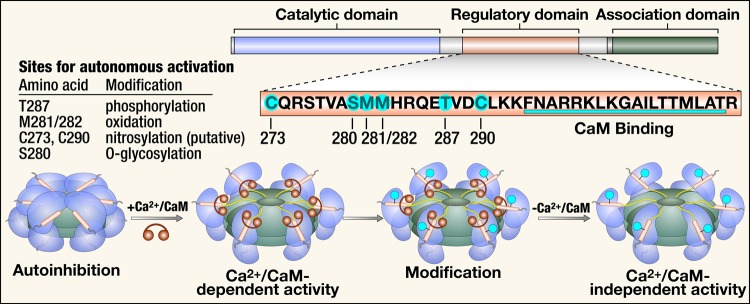
Figure 1.
Structure, activation, and post-translational modifications of CaMKII. CaMKII monomers consist of a catalytic domain, a regulatory domain, and an association domain. The regulatory domain has an autoinhibitory binding region with several sites for post-translational modification and a CaM binding region. Co-assembly of monomers through the association domain forms the CaMKII holoenzyme. In the presence of Ca2+, Ca2+/CaM binds to the regulatory site, which causes a conformational change and activation of the autoinhibited inactive enzyme with exposure of the catalytic domain. Post-translational modification of the autoinhibitory region at any of the sites highlighted results in constitutive activity of CaMKII that is autonomous of Ca2+/CaM. CaM, calmodulin.