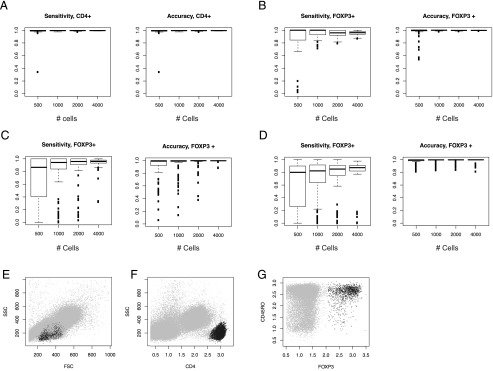
FIGURE 2.
Automatic gating of FOXP3+CD4+ T cells. Three clustering methods were compared for identifying FOXP3+CD4+ T cells: CD4+ T cell selection by HDDC, followed by FOXP3+ T cell selection by k-means (HK clustering); CD4+ T cell selection by HDDC, followed by FOXP3+ T cell selection by HDDC (HH clustering); and FOXP3+CD4+ T cell selection by one step-HDDC (one-step H clustering). Various random number seeds were used to resample events from flow cytometric data, and resampling was repeated 100 times for each random number seed, to address the robustness and efficiency of the three clustering methods. Sensitivities and accuracies were calculated by assuming that the manual gating provides a gold standard. (A–C) Sensitivities and accuracies of HK and HH: (A) sensitivities and accuracies for identifying CD4+ T cells by HDDC (shared by HK and HH). (B and C) Sensitivities and accuracies of (B) k-means and (C) HDDC for identifying FOXP3+ T cells from the identified CD4+ T cell cluster (HK and HH, respectively). (D) Sensitivities and accuracies of HDDC for identifying FOXP3+ T cells from all cells (one-step H). (E–G) Representative plots of automatically gated FOXP3+CD4+ T cells by the HK clustering method for (E and F) CD4+ T cells and (G) FOXP3+ T cells. The clustered cells are shown by black dots.