Figure 1.
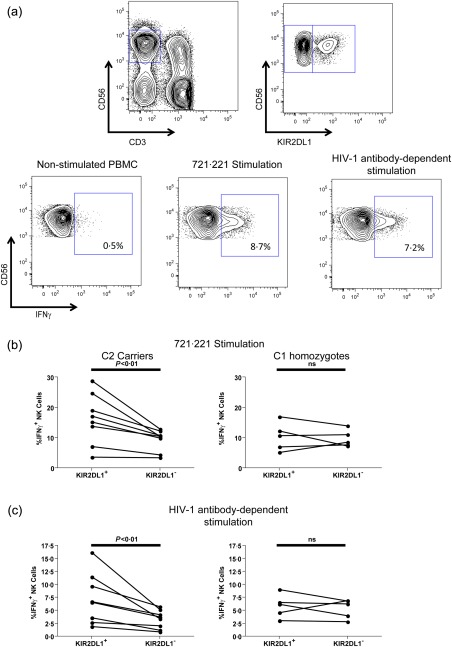
Direct and anti‐HIV‐1 antibody‐dependent activation of killer immunoglobulin‐like receptor (KIR)2DL1+ and KIR2DL1– natural killer (NK) cells from human leucocyte antigen (HLA)‐C2+ and HLA‐C1 homozygous donors. (a) Direct and anti‐HIV‐1 antibody‐dependent activation of NK cell effectors within peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was accomplished by stimulation with the HLA‐I‐devoid 721.221 cell line or HIV‐1AD8 gp140‐pulsed CEM.NKr‐CCR5 in the presence of anti‐HIV‐1 antibodies, respectively. Following stimulation PBMCs were stained with fluorochrome‐conjugated antibodies and assessed by flow cytometry. The fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) plots depict progressive gating upon CD3–CD56+ NK cells (top left), KIR2DL1+ and KIR2DL1– NK cell subsets (top right) and the assessment of gated cells for interferon (IFN)‐γ production in the non‐stimulated (bottom left), 721.221‐stimulated (bottom middle) and anti‐HIV‐1 antibody‐dependent stimulated conditions (bottom right). (b) Graphs depict the relative activation of the KIR2DL1+ and KIR2DL1– NK cell subsets upon activation by the 721.221 cell line in eight donors carrying HLA‐C2 alleles (left) and five HLA‐C1 homozygotes (right). (c) Graphs depict the relative activation of the KIR2DL1+ and KIR2DL1– NK cell subsets upon anti‐HIV‐1 antibody‐dependent activation in eight donors carrying HLA‐C2 alleles (left) and five HLA‐C1 homozygotes (right).
