Fig. 4.
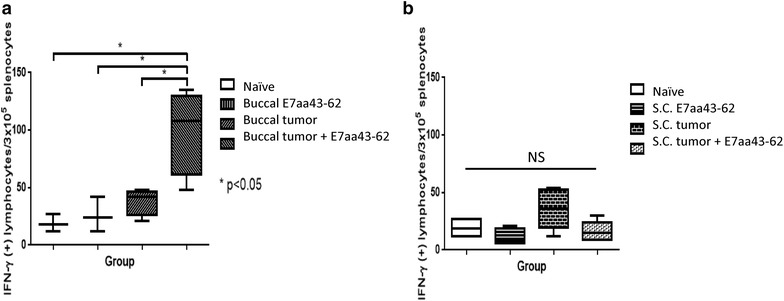
Comparison of HPV-16 E7 specific CD8+ T cell responses induced by synthetic HPV-16 E7aa 43-62 long peptide vaccine in various tumor model. C57BL/6 mice (five per group) received either 3 × 104 TC-1-Luc cells injection submucosally into the right buccal area or 1 × 105 TC-1-Luc cells injection subcutaneously into the abdomen. Three days after tumor injection, mice were vaccinated intratumorally with or without 50 μg of synthetic HPV-16 E7aa 43-62 peptide for four times in a 4-day intervals. 21 days after tumor injection, spleenocytes were harvested and stimulated with HPV16 E7aa49-57 peptide in the presence of GolgiPlug and IFN-γ-secreting CD8+ T cells were detected by intracellular cytokine staining followed by a flow cytometry analysis. a Bar graph depicting the amount of IFN-γ positive lymphocytes per 3 × 105 splenocytes for buccal treatments (mean ± SD). b Bar graph depicting the amount of IFN-γ positive lymphocytes per 3 × 105 splenocytes for subcutaneous treatments (mean ± SD). NS indicates not significant
