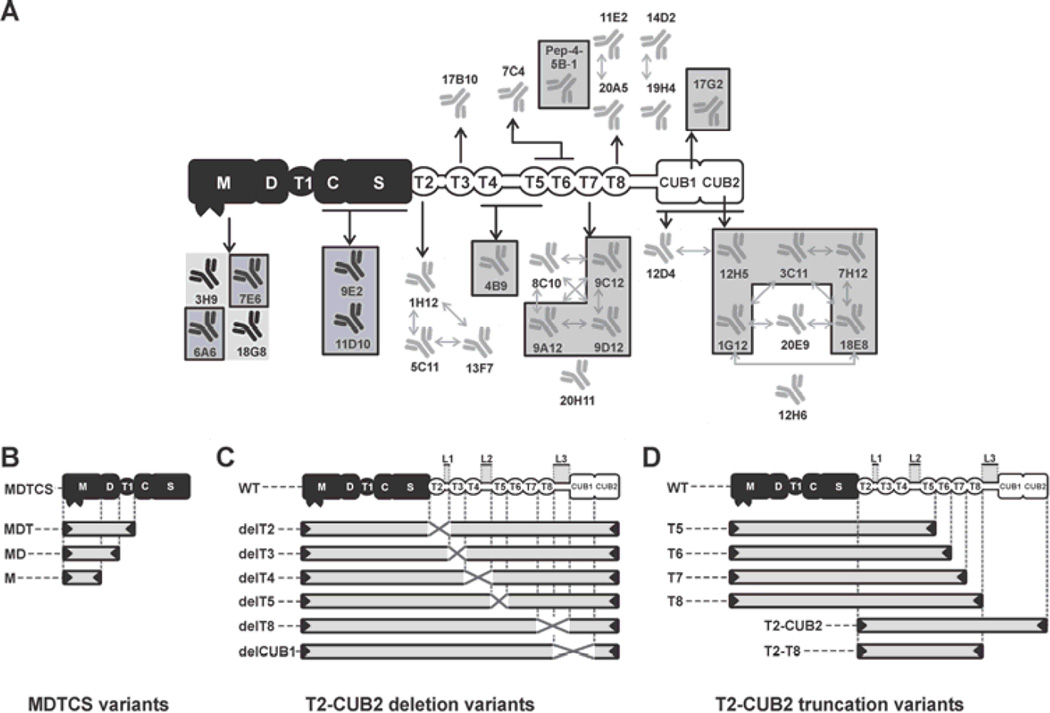
Fig. 1. Graphical representation of ADAMTS13 variants and epitope overview of the developed anti-ADAMTS13 mAbs.
The proximal MDTCS domains are represented in black and include a metalloprotease (M), disintegrin-like (D), thrombospondin type-1 repeat (T1), cysteine-rich (C) and spacer (S) domain. Distal (T2-CUB2) domains are represented in white and consist of seven thrombospondin type-1 repeats (T2 up to T8) and two CUB (Complement component C1r/C1s, Urinary epidermal growth factor (Uegf) and Bone morphogenic protein-1) domains. (A) Epitope overview of the reported and newly developed (indicated by a box) anti-ADAMTS13 mAbs. Abs with overlapping epitopes are indicated with arrows. (B, C and D) Graphical representation of the ADAMTS13 variants used in this study. (B) MDTCS variants MDTCS (W688X), MDT (Q499X), MD (W387X) and M (P285X). (C) WT and T2-CUB2 deletion (‘del’) variants. The linker regions between the T2–T3 domains (Linker 1), the T4–T5 domains (Linker 2) and the T8-CUB1 domains (Linker 3) are indicated by L1, L2 and L3 respectively. Deleted domains and linker regions are indicated by a cross. (D) T2-CUB2 truncation variants.