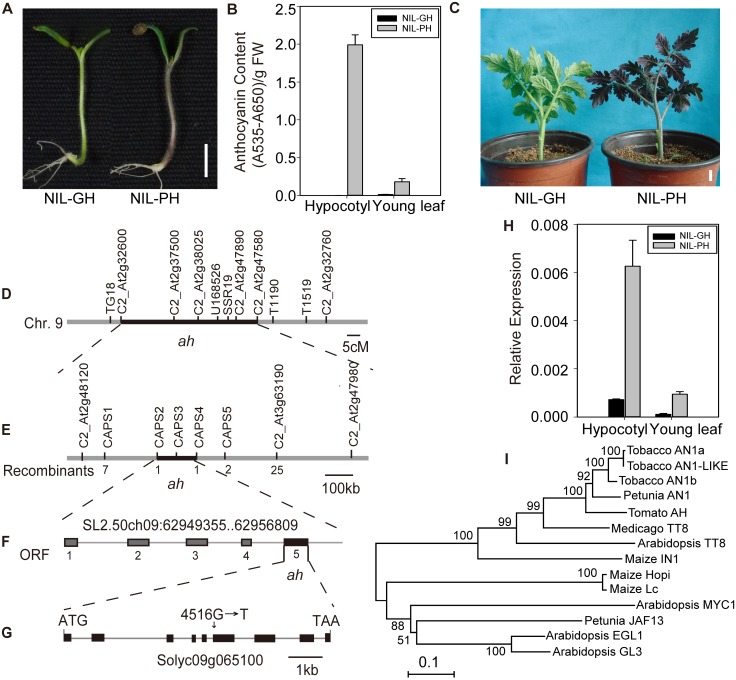
Fig 1. Map-based cloning of the ah locus.
(A) Phenotypes of the NIL seedlings. (B) Total anthocyanin content in hypocotyls and leaves of NIL-PH and NIL-GH plants. (C) The phenotype of 5-leaf-old NIL-PH and NIL-GH plants after growth in a phytotron under 16 h of light at 16°C/ 8 h of dark at 8°C for 20 days. (D) Coarse linkage map of the green locus on chromosome 9, and high-resolution linkage map of ah (E), with the number of recombinants between the molecular marker and ah indicated. (F) Annotation of the candidate region surrounding ah, with dark gray boxes indicating the putative genes predicted in ITAG2.40. (G) AH structure and the mutation site in FMTT271. The black boxes represent the coding sequences and lines between boxes represent introns. (H) Relative expression levels of AH in hypocotyls and leaves of NIL-PH and NIL-GH plants. A tomato ACTIN (Solyc03g078400) gene was used as the reference gene. The hypocotyls from 6-old day and the leaves from 5-leaf-day seedlings were used. (I) Phylogenetic tree of AH and other bHLH proteins from several plant species, constructed using the neighbor-joining method. The bHLH proteins and their respective GenBank accession numbers are as follows: petunia AN1, AAG25927; petunia JAF13, AAC39455; maize Lc, NP_001105339; Arabidopsis MYC1, NP_191957; tobacco AN1b, AEE99258; tobacco AN1a, AEE99257; Arabidopsis GL3, NP_680372; Arabidopsis EGL3, NP_176552; Arabidopsis TT8, CAC14865; maize IN1, AAB03841; Medicago TT8, XP_003590656; tobacco AN1-LIKE, NP_001289495; maize Hopi, CAB92300. NIL-PH (GH) refers to the plants from the NIL population with purple (green) in hypocotyls. Three biological replicates of all samples were analyzed. Scale bars, 1 cm.