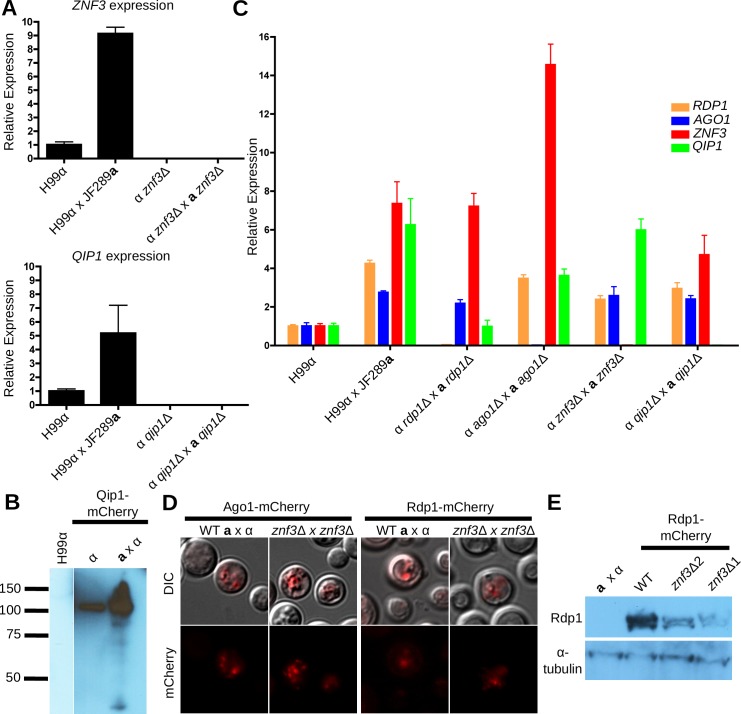
Fig 5. ZNF3 and QIP1 expression increases during mating.
(A) Expression of ZNF3 and QIP1 was determined using qPCR during vegetative growth and during mating. Expression of both increased in mating conditions. Strains used for ZNF3 expression: H99, H99 x JF289a, MF65, and XW205 x MF65. Strains used for QIP1 expression: H99, H99 x JF289a, SEC3, and SEC1 x SEC3. B) Increased protein levels of Qip1 were also detected via western blot analysis during mating. Strains used: H99, MF190, and MF190 x JF289a. (C) Expression of the canonical RNAi components and ZNF3 were determined via qPCR in bilateral crosses with mutations of the RNAi components. Loss of ago1Δ resulted in increased expression of ZNF3. Strains used: H99, H99 x JF289a, YPH348 x YPH351 (rdp1Δ), YPH738 x YSB299 (ago1Δ), MF62 x MF65 (znf3Δ), and SEC1 x SEC3 (qip1Δ). (D) Ago1-mCherry and Rdp1-mCherry direct fluorescence signals in wild type vs. znf3Δ x znf3Δ co-cultures under mating conditions. Mating mixtures were spotted and incubated on V8 (pH = 5) plates for 24 hours in the dark and then cells were scraped off and resuspended in water for microscopy. Strains used for Ago1: XW35 x YL99a and MF201 x MF62. Strains used for Rdp1-mCherry: XW37 x YL99a and MF197 x MF62. (E) Western blotting for Rdp1-mCherry shows that levels of Rdp1 are modestly decreased in a znf3Δ mutant compared to wild type. Strains used: H99 x JF289a, XW37 x JF289a, MF197 x MF62, and MF198 x MF62.