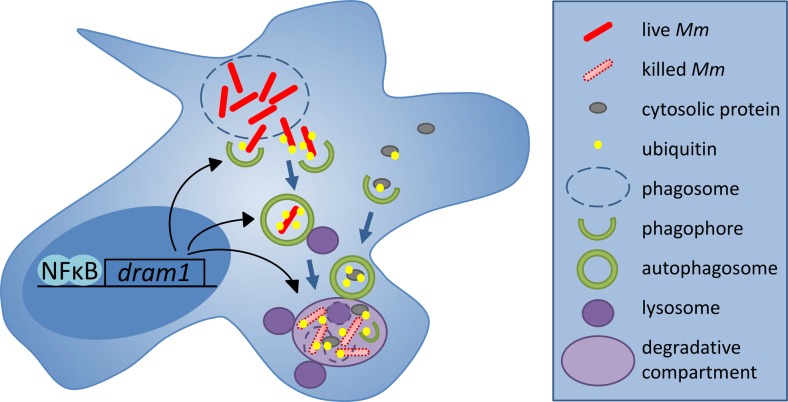
Fig. 3.
Dram1-modulated autophagic defense pathway in macrophages. Following infection of zebrafish embryos, Mm bacteria are detected inside membrane compartments of macrophages as well as freely in the cytoplasm [57, 86]. Translocation of Mm to the cytoplasm is dependent on the ESX-1 secretion system required for rupture of the phagosome membrane (dashed line). By analogy with studies of Mtb in cultured macrophages, Mm bacteria escaping the phagosome are thought to be ubiquitinated by a STING-dependent pathway and targeted to selective autophagy mediated by ubiquitin receptors [57, 124]. DRAM1 is induced during infection by Myd88-NFκB signaling and proposed to promote the formation of autophagosomes as well as multiple vesicle fusion events between autophagosomes and lysosomes leading to the formation of larger degradative compartments [57, 125]. The microbicidal properties of these compartments could be enhanced due to the delivery of ubiquitinated peptides by autophagosomes [126]