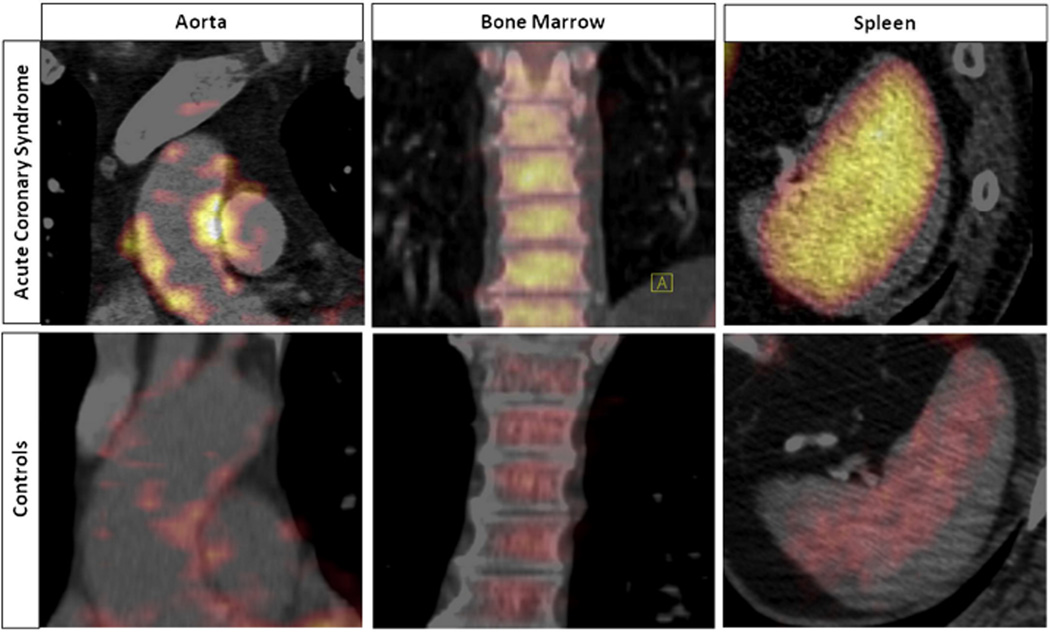
Figure 4. Activation of Glucose Uptake in the Arterial Wall, Spleen, and Bone Marrow in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes.
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FdG) uptake increased significantly in the arterial wall (aorta), bone marrow, and spleen in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) versus control subjects. Reprinted from Emami et al. (67).