Abstract
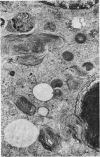
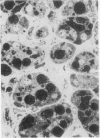
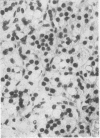
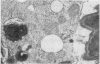
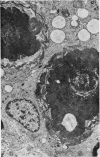
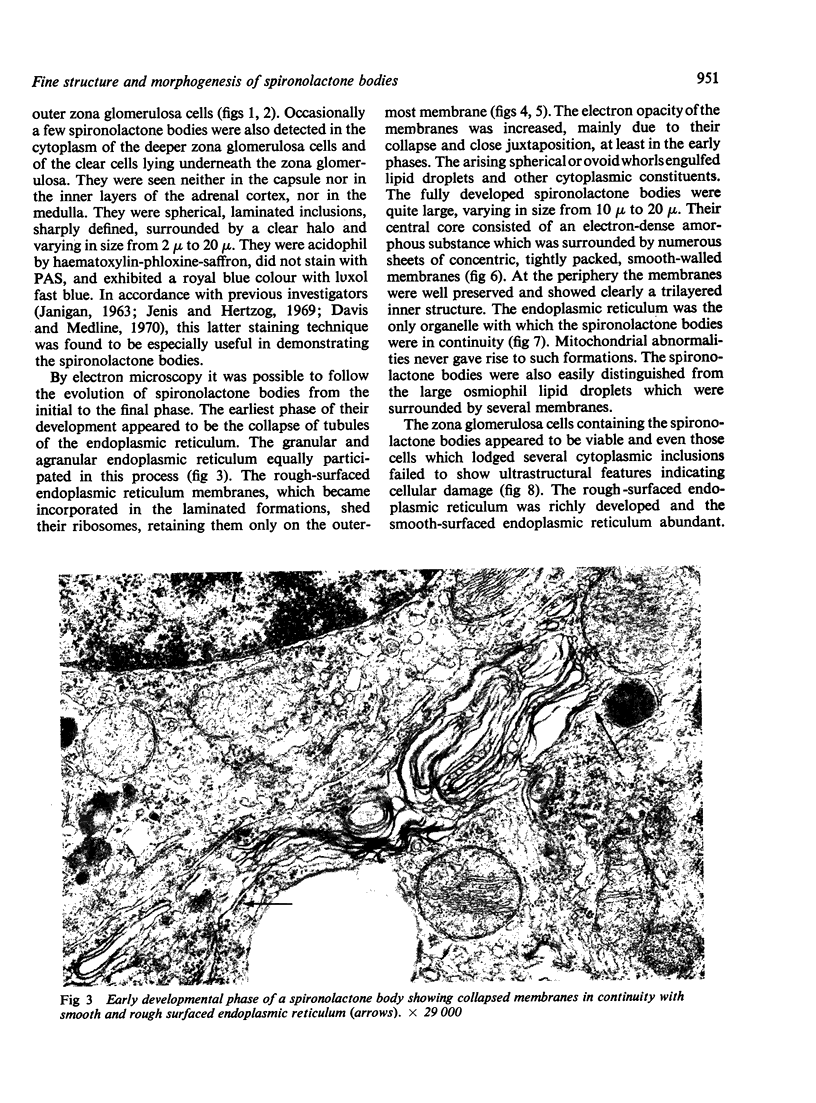
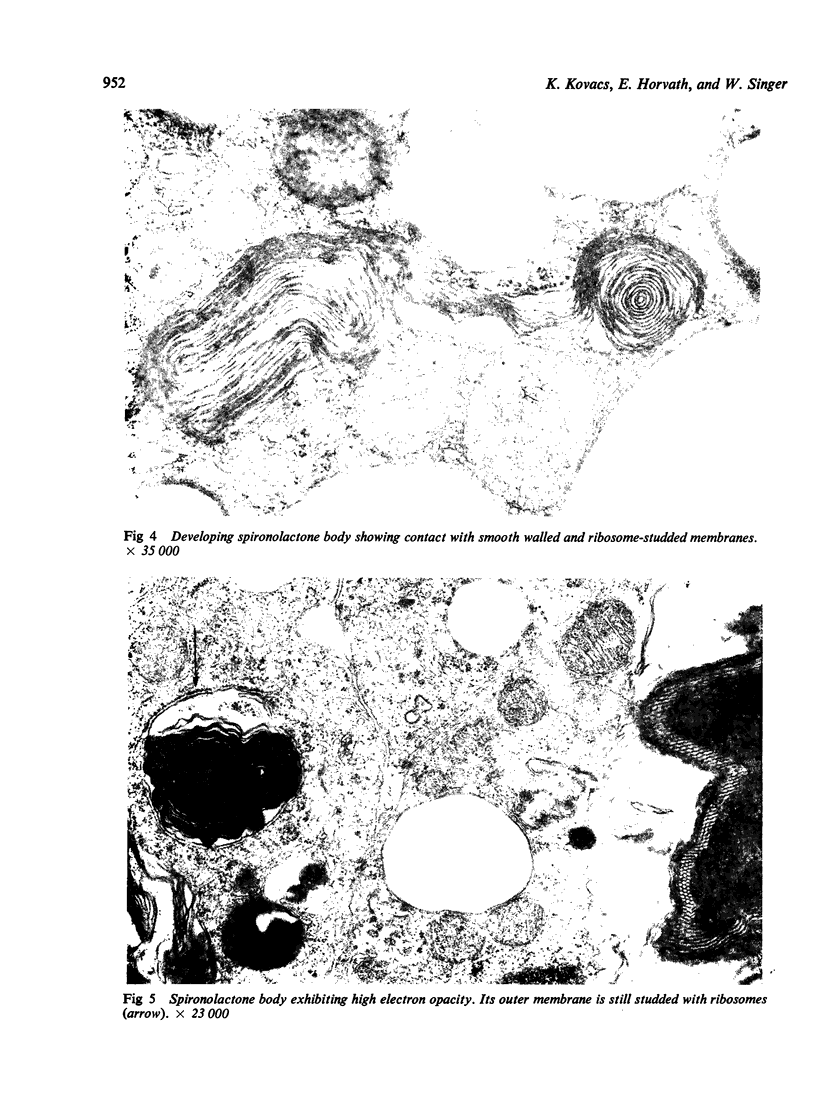
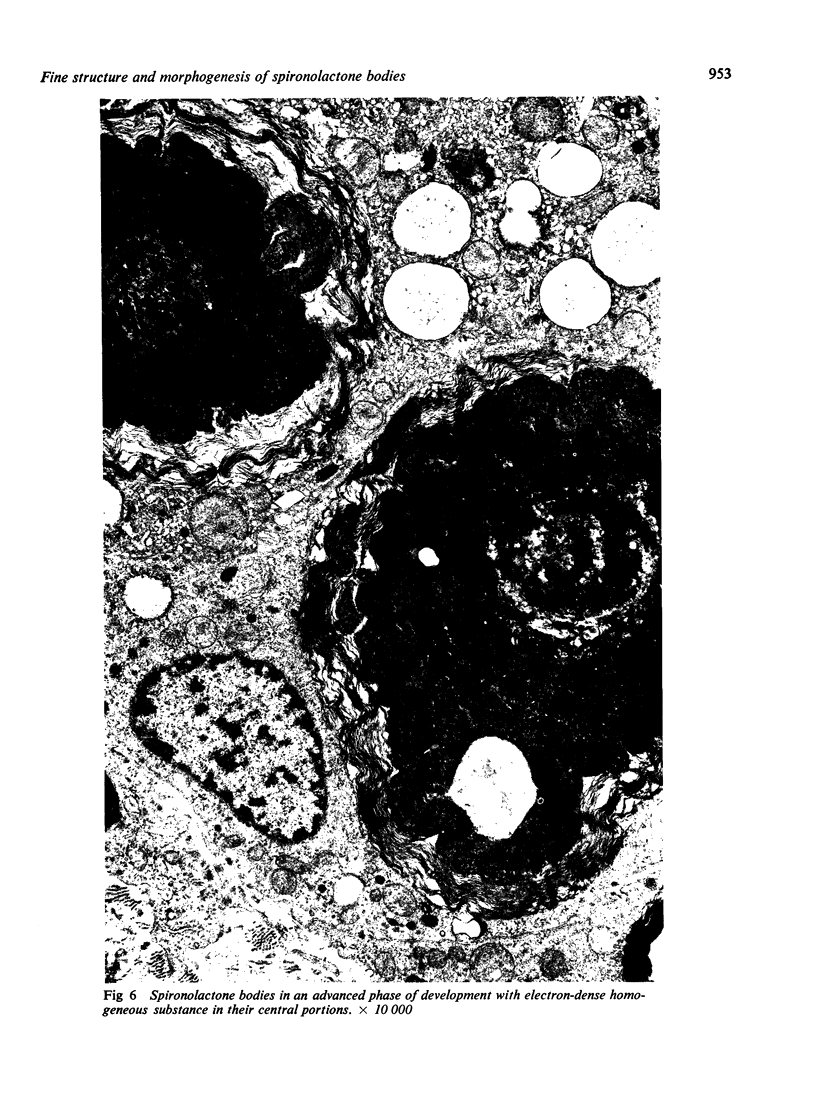
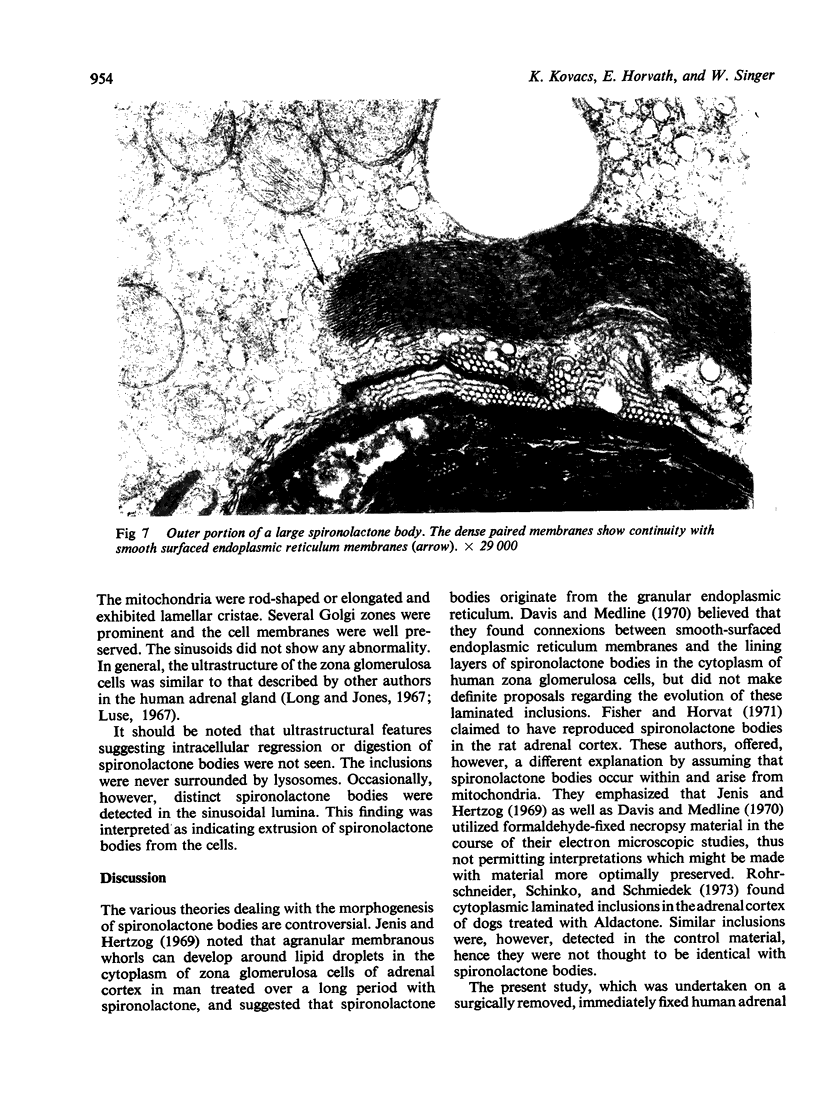
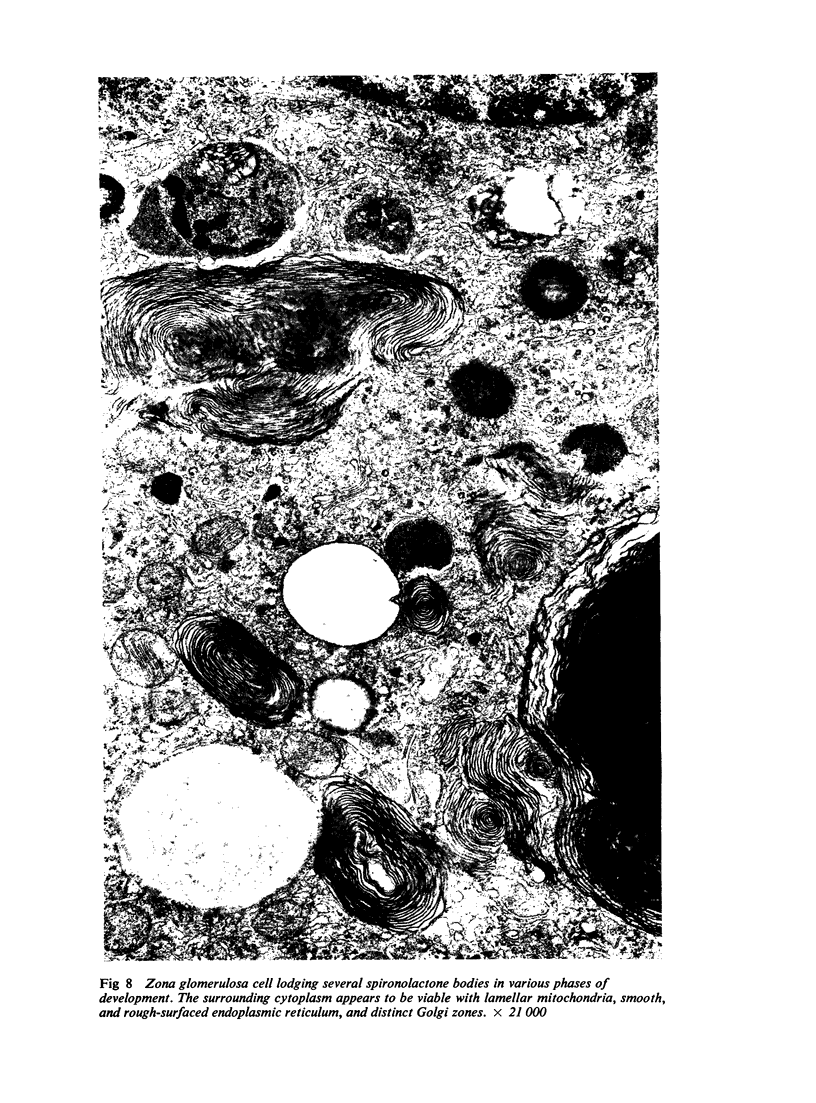
Numerous spironolactone bodies have been detected in the zona glomerulosa cells of the adrenal cortex of a 36-year-old spironolactone-treated woman whose non-tumorous right adrenal gland was removed surgically because of primary hyperaldosteronism. Electron microscopy revealed spherical laminated whorls which consisted of a central core composed of an amorphous electron-dense material surrounded by numerous smooth-walled concentric membranes. Continuous with and deriving from the endoplasmic reticulum, they were present in viable cells and were not associated with ultrastructural features indicating cellular injury. Cytoplasmic inclusions similar to spironolactone bodies can be detected in other organs after the administration of various compounds. Thus, they can be regarded as neither specific to spironolactone treatment nor exclusively inducible in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis D. A., Medline N. M. Spironolactone (aldactone) bodies: concentric lamellar formations in the adrenal cortices of patients treated with spironolactone. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Jul;54(1):22–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. R., Horvat B. Experimental production of so-called spironolactone bodies. Arch Pathol. 1971 May;91(5):471–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg B. D., Kovacs K., Tuchweber B. Ultrastructural changes in the rat liver following protracted treatment with pregnenolone-16 -carbonitrile and digitoxin. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1972;12(1):61–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02893986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Slesers A., Hopkins E. Drug-induced and naturally occurring myeloid bodies. Lab Invest. 1972 Jul;27(1):62–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANIGAN D. T. Cytoplasmic bodies in the adrenal cortex of patients treated with spirolactone. Lancet. 1963 Apr 20;1(7286):850–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenis E. H., Hertzog R. W. Effect of spironolactone on the zona. Light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol. 1969 Nov;88(5):530–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs K., Blascheck J. A., Yeghiayan E., Hatakeyama S., Gardell C. Adrenocortical lipid hyperplasia induced in rats by aniline. A histologic and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jan;62(1):17–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs K., Horvath E., Szabo S., Garg B. D., Tuchweber B. Cycloheximide-induced ultrastructural changes in the corpus luteum of rats. Experientia. 1973;29(7):839–840. doi: 10.1007/BF01946319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs K., Khandekar J. D., Szabo S., Garg B. D., Gardell C., Tuchweber B. Formations lamellaires dans le cortex surrénalien du rat. Arch Biol (Liege) 1971;82(3):211–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs K., Khandekar J. D., Szabó S., Garg B. D., Tuchweber B. Effect of cycloheximide on the rat adrenal cortex: a light and electron microscopic study. Rev Can Biol. 1972 Jun;31(2):105–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE G. W. Aldosterone antagonists. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Dec;102(6):998–1004. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00260230144018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. A., Jones A. L. Observations on the fine structure of the adrenal cortex of man. Lab Invest. 1967 Oct;17(4):355–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marek J., Thoenes W., Motlík K. Lipoide Transformation der Mitochondrien in Nebennierenrindenzellen nach Aminoglutäthimid (Elipten Ciba) Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1970;6(2):116–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider I., Schinko I., Schmiedek P. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Zona glomerulosa des Hundes nach Behandlung mit Spirolacton. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1973;159(4):321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01851606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER J. W., MIYAI K., PHILLIPS M. J. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF MEMBRANE-PARTICLE ARRAYS IN LIVER CELLS OF ETHIONINE-INTOXICATED RATS. Am J Pathol. 1964 Feb;44:169–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikata T., Kanetaka T., Endo Y., Nagashima K. Drug-induced generalized phospholipidosis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1972 Aug;22(3):517–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1972.tb01849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spark R. F., Dale S. L., Kahn P. C., Melby J. C. Activation of aldosterone secretion in primary aldosteronism. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):96–104. doi: 10.1172/JCI105978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]