Fig. 5.
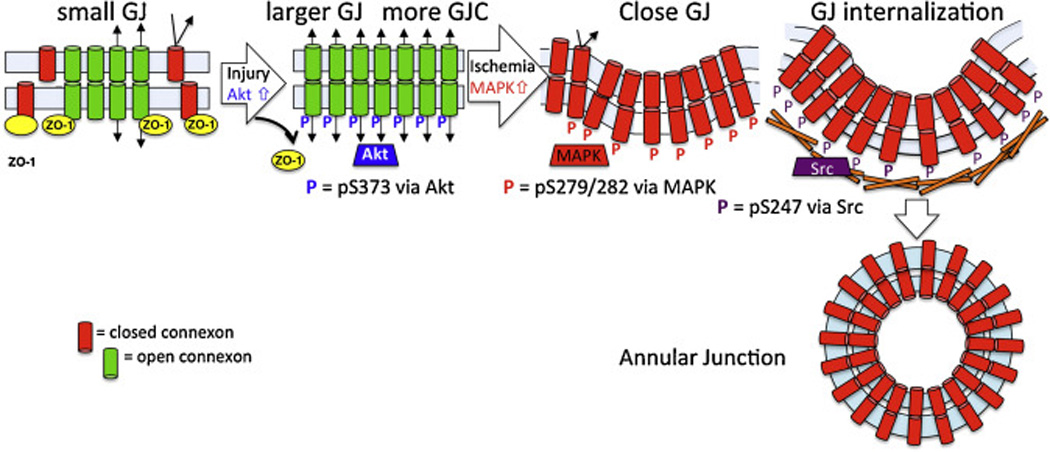
Model of the steps in gap junction turnover regulated by Cx43 phosphorylation. Our model predicts that phosphoS373 (via Akt, shown in blue) first promotes Cx43 accumulation into larger GJs with increased gap junctional communication. Larger junctions could promote annular junction formation through decreased membrane and energy restraints compared to that needed for smaller vesicles. Next, phosphoS279/282 (via MAPK, shown in red) closes the gap junction and then phosphoY247 (via Src, shown in purple) initiates recruitment of the internalization machinery – a timeline consistent with the observed kinetics of phosphorylation at these sites in response to EGF, TPA or wounding.
