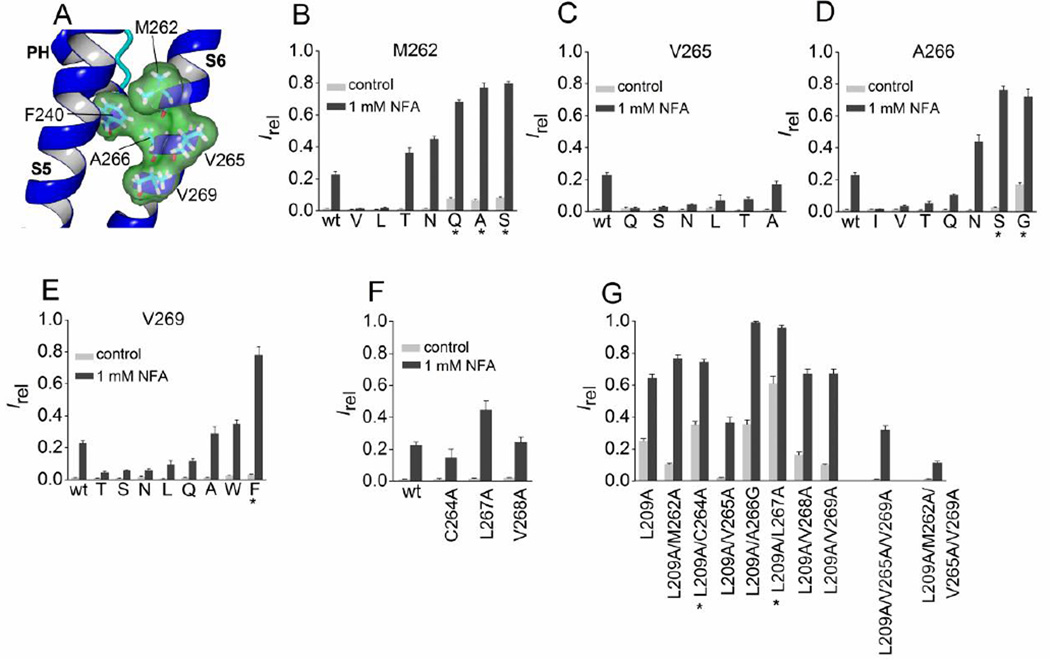
Fig. 7.
Mutation analysis of S6 segment residues predicted to be in close proximity to Phe-240. (A) Slo2.2-based homology model of the pore helix and S6 segment of a Slo2.1 subunit, highlighting the close proximity of four residues in the S6 segment to Phe-240 in the pore helix. (B–F) Irel measured at 0 mV in the absence (control) or presence of 1 mM NFA for wt channels (n = 14), Met-262 mutant channels (B, n = 5–9), Val-265 mutant channels (C, n = 5–9), Ala-266 mutant channels (D, n = 3–8), Val-269 mutant channels (E, n = 3–7), and point mutations in S6 as indicated (F, n = 5–9). (G) Irel measured at 0 mV in the absence (control) and presence of 1 mM NFA for L209A channels containing an additional one or more Ala substitution of the indicated S6 residue(s) (n = 7–8). For panels B–E, amino acid substitutions of the indicated native residue are indicated by single letter code. *, indicates an increase (p < 0.01) in both measures of Irel compared to wt channels, or L209A in panel G. Error bars indicate + S.E.