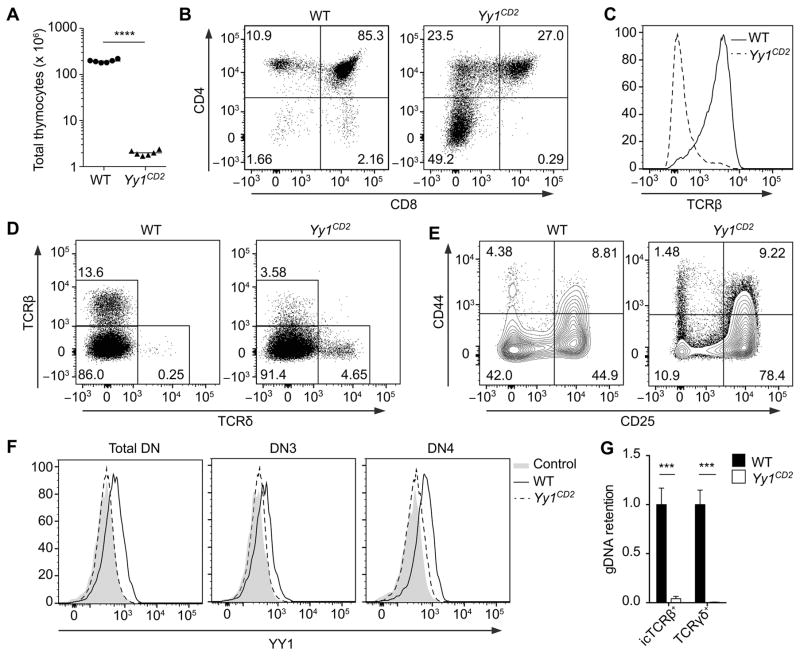
Figure 1. Early ablation of Yy1 severely blocks T cell development.
(A) Number of total thymocytes in Yy1f/f (WT) and Yy1f/f CD2-Cre (Yy1CD2) mice. Each data point represents an individual mouse and the horizontal line indicates the mean. Statistical significance was evaluated by unpaired Student’s t-test. (B–F) Flow cytometry analysis of thymocytes from WT and Yy1CD2 littermates. (B) CD4 and CD8 staining is shown for total thymocytes. (C) TCRβ staining is shown for pre-gated CD4+CD8− thymocytes. (D) TCRβ and TCRδ staining is shown for total thymocytes. (E) CD44 and CD25 staining is shown for pre-gated CD4−CD8−Lin− thymocytes. (F) Intracellular staining of YY1 in pre-gated DN (CD4−CD8−Lin−), DN3 (CD4−CD8−Lin−CD25+CD44−) and DN4 (CD4−CD8−Lin−CD25−CD44−) thymocytes. The control consists of WT thymocytes incubated with anti-YY1 without fluorescent secondary antibody. Data are representative of three (B–E) or two (F) independent experiments. (G) Genomic DNA was extracted from sorted icTCRβ+ or TCRγδ+ thymocytes and deletion of Yy1 exon1 was measured by real-time PCR with normalization to Cd14. Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3 samples for each genotype. Statistical significance was evaluated by unpaired Student’s t-test with Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.