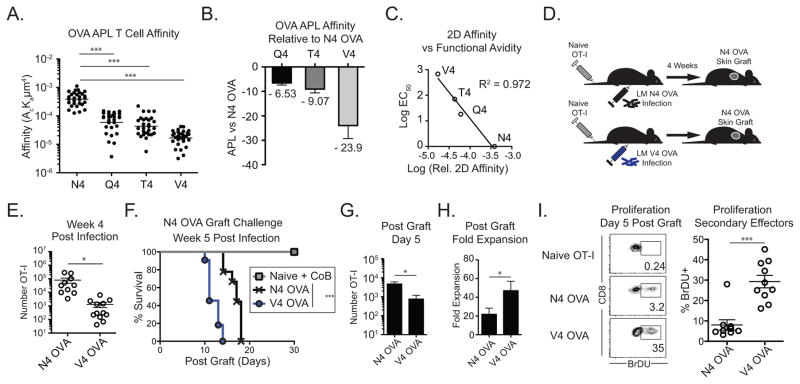
Figure 1. Low affinity primed CD8+ T cells mount potent secondary responses against high affinity grafts.
(A–C) The relative 2D affinity of naïve OT-I T cells to N4 OVA, Q4 OVA, T4 OVA, and V4 OVA H-2b were measured using a micropipette. (A) Relative 2D affinity of OT-I T cells to N4 OVA and OVA APLs (B) Fold difference in 2D affinity between N4 OVA and OVA APLs. (C) Linear association between relative 2D affinity and reported relative functional avidity. (D–H) Naïve mice adoptively transferred with 104 OT-I T cells were infected the following day with either LM-N4 OVA or LM-V4 OVA. Naïve mice or mice containing N4 OVA or V4 OVA primed memory OT-I cells were transplanted with N4 OVA skin grafts 5 weeks post infection. (E) Frequency of memory N4-OVA and V4 OVA primed memory OT-I cells in pooled secondary lymphoid organs (N4 OVA vs V4 OVA p<0.001). (F) N4 OVA skin graft survival in LM-N4 OVA or LM-V4 OVA infected mice. Naïve mice were treated with CTLA-4 Ig and anti-CD154 costimulation blockade (N4 OVA vs V4 OVA groups p<0.0003). (G) Number of N4 OVA or V4 OVA primed OT-I cells recovered in the draining LNs on day 5 post-graft. (H) Fold expansion of N4 OVA and V4 OVA primed memory cells from day 0 to day 5 post graft. (I) Frequency of BrDU+ cells among N4 OVA or V4 OVA primed secondary effectors on day 5 following skin graft, or in ungrafted naïve OT-I controls. Data compiled from at least 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05, ***p<0.0001. LM, Listeria monocytogenes. CoB, costimulation blockade.