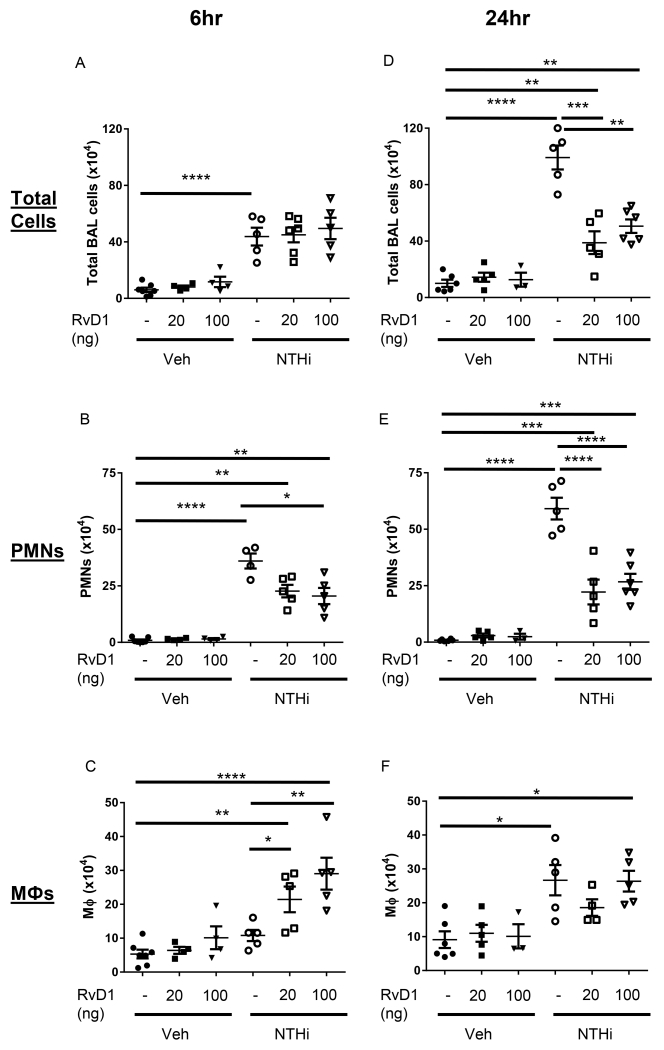
Fig. 2. AT-RvD1 shifts the profile of inflammatory cell influx.
Differential cell counts were determined from bronchoalveolar lavage of AT-RvD1 (20 or 100ng/mouse, OA) and/or NTHi (1 × 106 CFUs, OA) inoculated mice. Total cell (A, D), neutrophil (B, E), and macrophage (C, F) counts were evaluated at 6hrs (A-C) and 24hrs (D-F). Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA (overall p<0.0001 NTHi [all panels], p= 0.0055 AT-RvD1 [B], p=0.0021 AT-RvD1 [C], p<0.0001 AT-RvD1 [D, E]) with Bonferroni’s posttest for multiple comparisons (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001), n=5-8 mice/group.