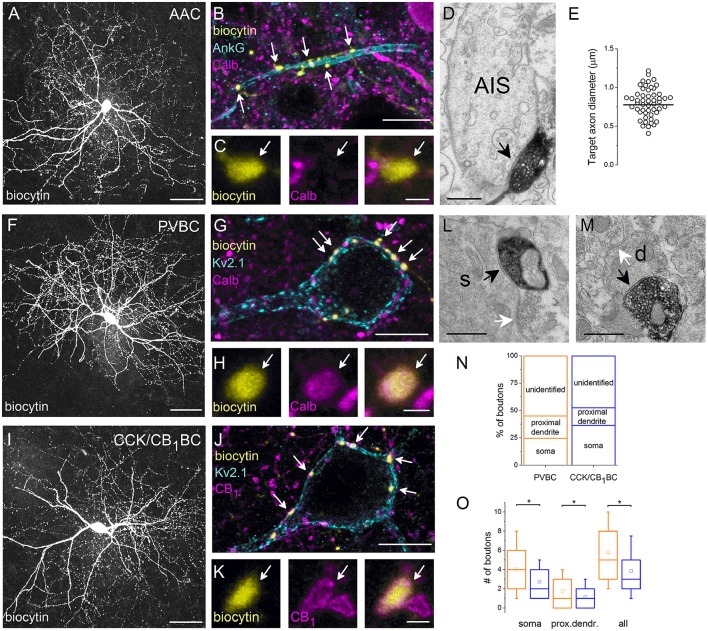
Figure 3.
Neurochemical content and postsynaptic targets of interneurons innervating the perisomatic region of principal cells in the BLA. Maximum z intensity projection images taken of an in vitro biocytin-filled AAC (A), PVBC (F), or CCK/CB1BC (I). (B) Varicosities of the AAC in (A) contact with an AIS visualized by ankyrin G staining and lack Calb immunoreactivity (C). (D) A biocytin-filled bouton of an AAC forms a symmetrical synapse on an AIS. (E) Distribution of target axon diameters obtained by random sampling (55 boutons from 7 AACs). Black lines represent the mean value. (G) The biocytin-containing boutons of the same cell as in (F) form close contacts with the Kv2.1-labeled perisomatic region of a PC and express Calb (H). (J) The boutons of the interneuron in (I) form close appositions with the Kv2.1-immunostained membranes of a PC and express CB1 (K). (L, M) Electron micrographs show biocytin-labeled axon terminals of a PVBC forming symmetrical synapses on a soma (s) or a small caliber dendrite (d; black arrows). The same postsynaptic elements also received symmetrical synapses from unlabeled axon endings (white arrows). (N) Ratio of boutons of PVBCs (n = 12) and CCK/CB1BCs (n = 12) forming close contacts with Kv2.1-immunostained somata, proximal dendrites, or which did not appose any Kv2.1-immunostained profiles (unidentified). Note, that the high ratio of boutons contacting the perisomatic region of PCs defines the cells as BCs. (O) A larger number of boutons from PVBCs (orange) than from CCK/CB1BCs (blue) contact the perisomatic region of individual PCs. Asterisks mark significant differences (for values see the text). The mean (small open square), the median (midline of the box), the interquartile range (box), and the 5/95% values (ends of whisker bars) are plotted. AAC, axo-axonic cell; PVBC, parvalbumin-containing basket cell; CCK/CB1BC, cholecystokinin and CB1 cannabinoid receptor-expressing basket cell. Scale bars, 50 μm in (A,F,I), 10 μm in (B,G,J); 1 μm in (C,H,K); 0.5 μm in (D,L,M).