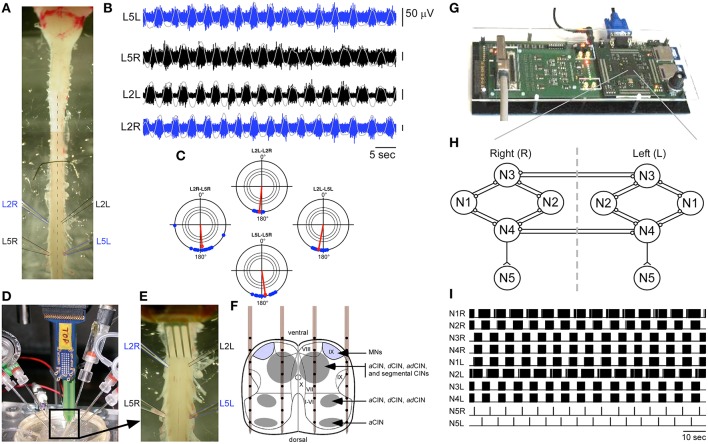
Figure 1.
Experimental paradigm. (A) Neonatal rat preparation. (B) Example of locomotor-like activity on bilateral L2 and L5 ventral roots. Integrated and smoothed traces are superimposed in gray. (C) This rhythm can be represented as four polar plots showing the antiphase relationship (180° angle in the plot) between two recordings of same level ipsi and contralateral ventral roots, as well as between two levels on the same side. In each plot, the three concentric circles indicate significance levels of the Rayleigh test at P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001. (D,E) View of the experimental setup showing simultaneous ventral root recordings and a 4-shank multichannel neural probe inserted at L1 level for ISMS. (F) Schematic representation of the neural probe in the transverse plane of the lumbar spinal cord adapted from Kiehn and Butt (2003). MNs, Motoneurons; CINs, Commissural interneurons; a, ascending; d, descending. (G) The multimed platform housing the artificial CPG implemented in an FPGA. (H) Structure of the artificial CPG (“o” connections are inhibitory, “<” connections are excitatory). (I) Example of the activity of all neurons of the artificial CPG. Neurons N5L and N5R were used to trigger ISMS at the time of every of their spikes.