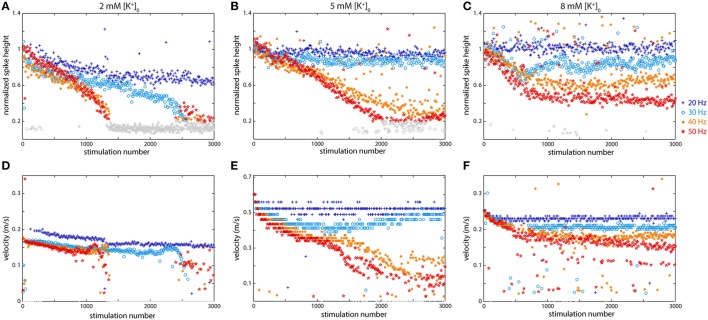
Figure 5.
Potassium concentration affects axonal propagation at higher frequencies including both the spike height (A–C) and the propagation velocity (D–F). (A,D) Low K+ concentration 2 mM) caused much more dramatic effects and propagation failures than regular conditions. (B,E) Regular (5 mM) K+ concentration in the medium. (C,F) High K+ concentration (8 mM) also altered axonal behavior, but not as dramatically. Propagation velocity was affected by K+ concentration: both higher and lower [K+] slowed propagation.