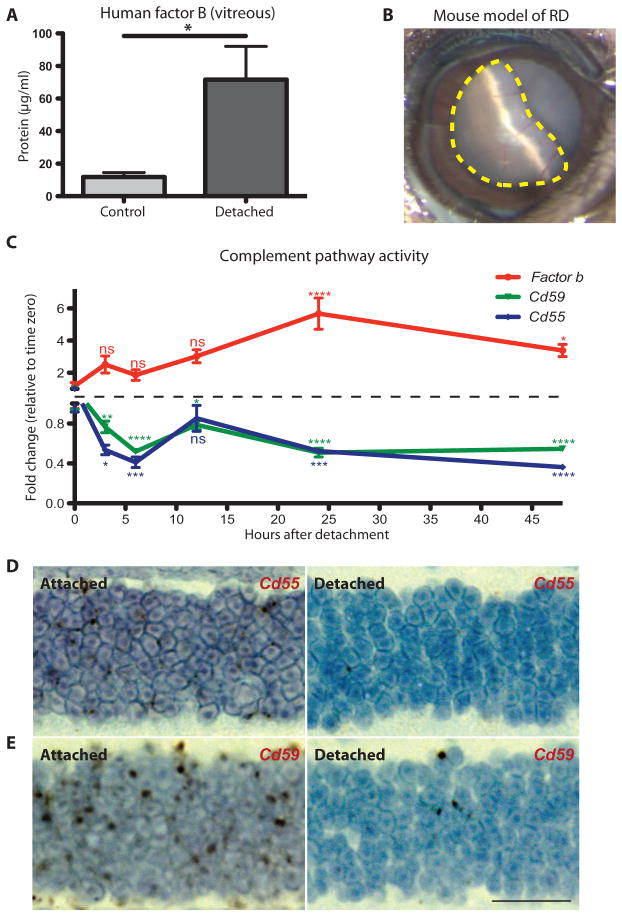
Fig. 1. Activity of the alternative complement pathway during RD.
(A) ELISA analysis of factor B production in human vitreous from patients with RD (n = 10) compared to nondetached retina control patients with a macular hole or epiretinal membrane (n = 4). (B) Image of RD in a mouse model. The dotted yellow line outlines the region of retina that is detached (about 60%). (C) Time course of gene expression for Fb (encoding factor B), Cd55, and Cd59 in the retina of mice after RD. The red line tracks Fb gene expression, the blue line tracks Cd55 expression, and the green line tracks Cd59 expression at intervals over a period of 48 hours. Color of asterisks corresponds to the gene (n = 4 for each time point). (D) Representative 3,3′-diaminobenzidine labeling (brown) for Cd55 mRNA expression in the attached outer nuclear layer (left panel) and the detached outer nuclear layer (right panel) of the same eye (n = 4). (E) 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine labeling (brown) for Cd59 mRNA expression in the attached outer nuclear layer (left panel) and the detached outer nuclear layer (right panel) of the same eye (n = 4). ns, not significant. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001; unpaired Student’s t test. Scale bar, 20 μm.