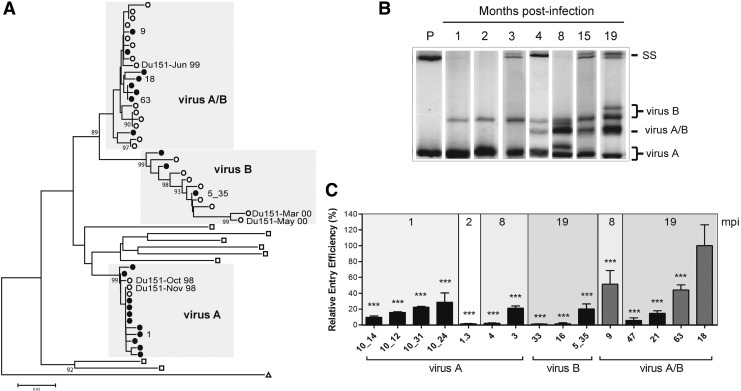
FIG. 1.
Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of the viruses infecting Du151. (A) Neighbor-joining tree of the C2–C3 region of the env Du151 clones to demonstrate that strains A and B are phylogenetically distinct. The neighbor-joining tree was generated using Mega543 with HXB2-LAI-IIIB-BRU (△) and those from the South African CAPRISA subtype C cohort44 (□) as a reference. Sequences included functional env clones (●) and published Du151 sequences (◯).29 Functional env clones mentioned in the text are labeled. (B) The virus A env C2–C3 region was used as a radiolabeled probe to track the emergence of genetic diverse strains over the course of infection (1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 15, and 19 mpi) using HTA analysis. SS, single stranded bands; P, probe. The parent viruses (A and B) and the recombinant virus (A/B) are indicated. (C) The 15 functional env genes were used to generate pseudovirions and tested for differences in entry efficiency using TZM-bl cells. Results were plotted as the percent entry efficiency of clone C18. Virus A/B clones C9, C63, and C18 are indicated in gray. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's posttest (***p<0.001 compared to C18) using GraphPad Prism 5 software.