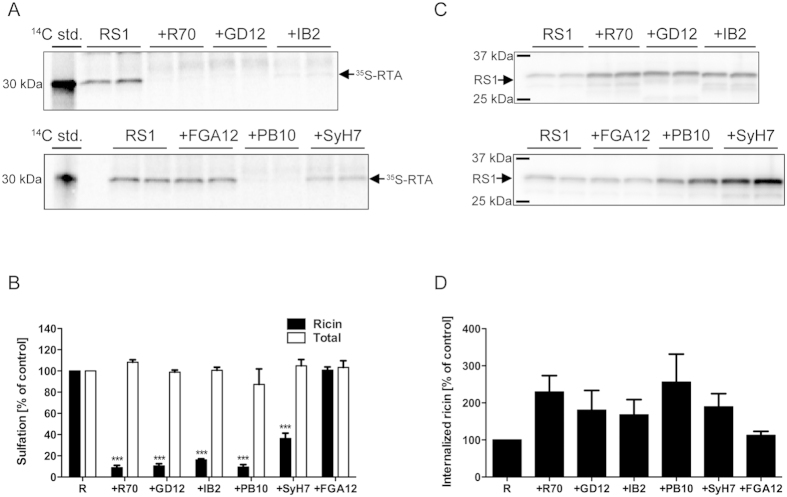
Figure 3. Inhibition of ricin trafficking to the TGN by R70, SyH7 and other toxin-neutralizing, RTA-specific mAbs.
HeLa cells were incubated with Na235SO4 prior to the addition of RS1 in the absence or presence of the indicated mAbs. Two hours later the cells were washed with buffer containing lactose (0.1 M) to remove residual surface-bound ricin and then lysed. Precipitated proteins from lysates, as well as a14C-methylated protein molecular weight standard, were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane. Specific RTA sulfation was measured by autoradiography (A) and quantitated by densitometry (B). Total sulfation was determined by precipitation of the remaining lysate. Each bar (mean with SD) represents the average of three independent experiments. The asterisks (p < 0.01) represent significance between % sulfated ricin control and sulfated ricin plus mAb treatment, as determined using an unpaired t-test with a 95% confidence interval. While there were slight differences in total sulfation across the different treatment groups (100–115%), none of the differences observed were statistically significant. After the sulfation assay, the membrane was subjected to Western blot analysis with an anti-RTA antibody (C) and then quantitated by densitometry (D). The densitometry signals in presence of mAbs were normalized to the signal for RS1 alone, which was set to 100%.