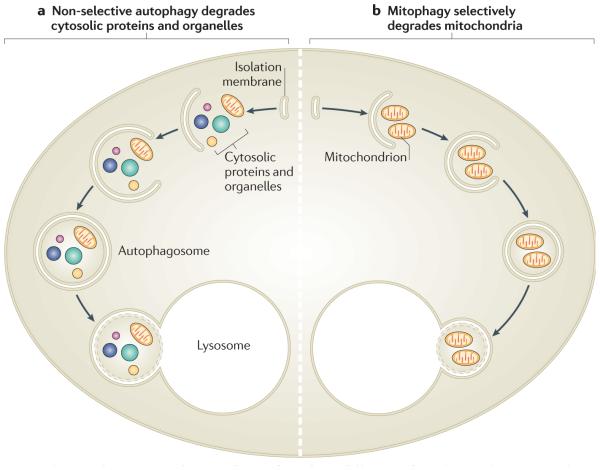
Figure 1. Non-selective autophagy and mitophagy have different roles.
a | Non-selective autophagy occurs when cells are deprived of nutrients. It degrades a range of cytosolic contents, including proteins and many types of organelles. After their recruitment into isolation membranes, cytosolic components are sealed into autophagosomes that fuse with lysosomes. The degradation of these components in the lysosome supplies building blocks for re-use and for metabolism to provide ATP. b | By contrast, mitophagy occurs to eliminate mitochondria, either to regulate their number or to specifically remove ones that are damaged. Mitochondria are selectively recruited into isolation membranes, which seal and then fuse with lysosomes to eliminate the trapped mitochondria.