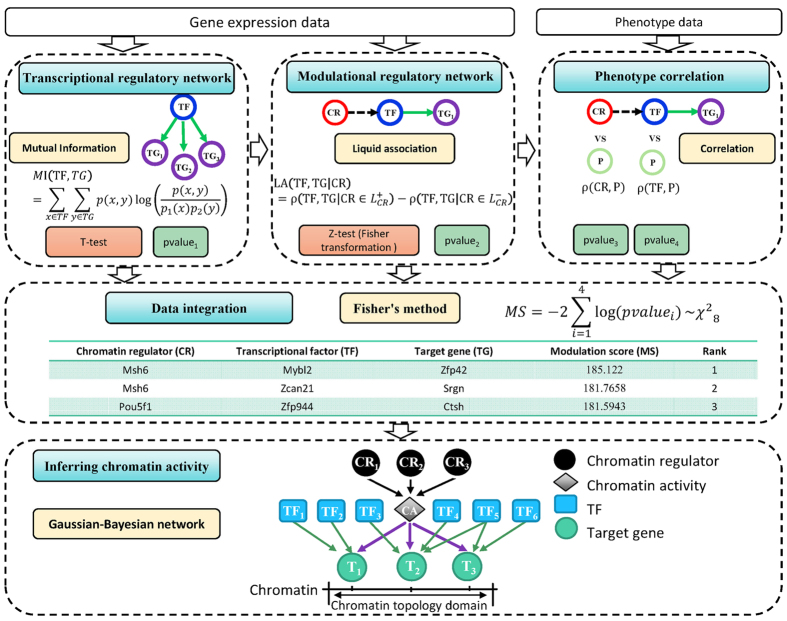
Figure 1. Workflow of MOCHA.
MOCHA is a method to identify CRs’ modulation role in transcriptional regulation. MOCHA takes gene expression data and phenotype data as input. It will output the chromatin activities in each genomic region and their corresponding chromatin regulators. All the triplets composed of chromatin regulator (CR), transcriptional factor (TF), target gene (TG) (modulation on a single target gene) are ranked by an integrative modulation score. Given a triplet, it computes modulation score by integrating the transcriptional regulation strength, interaction of transcriptional regulation and chromatin regulator, consistence of chromatin regulator expression and phenotype, and consistence of TF expression and phenotype. All the four lines of evidence can be evaluated by p-values and further combined into a single modulation score by Fisher’s method. We then rank all the triplets by their modulation scores. At last, the significant triplets are integrated into a graphical model according to their target gene’s genomic location to infer the chromatin activity of each chromatin region.